Ezrin interacts with S100A4 via both its N- and C-terminal domains
- PMID: 28493957
- PMCID: PMC5426754
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177489
Ezrin interacts with S100A4 via both its N- and C-terminal domains
Abstract
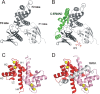
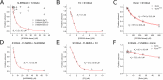
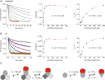
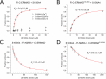
Ezrin belongs to the ERM (ezrin, radixin, moesin) protein family that has a role in cell morphology changes, adhesion and migration as an organizer of the cortical cytoskeleton by linking actin filaments to the apical membrane of epithelial cells. It is highly expressed in a variety of human cancers and promotes metastasis. Members of the Ca2+-binding EF-hand containing S100 proteins have similar pathological properties; they are overexpressed in cancer cells and involved in metastatic processes. In this study, using tryptophan fluorescence and stopped-flow kinetics, we show that S100A4 binds to the N-terminal ERM domain (N-ERMAD) of ezrin with a micromolar affinity. The binding involves the F2 lobe of the N-ERMAD and follows an induced fit kinetic mechanism. Interestingly, S100A4 binds also to the unstructured C-terminal actin binding domain (C-ERMAD) with similar affinity. Using NMR spectroscopy, we characterized the complex of S100A4 with the C-ERMAD and demonstrate that no ternary complex is simultaneously formed with the two ezrin domains. Furthermore, we show that S100A4 co-localizes with ezrin in HEK-293T cells. However, S100A4 very weakly binds to full-length ezrin in vitro indicating that the interaction of S100A4 with ezrin requires other regulatory events such as protein phosphorylation and/or membrane binding, shifting the conformational equilibrium of ezrin towards the open state. As both proteins play an important role in promoting metastasis, the characterization of their interaction could shed more light on the molecular events contributing to this pathological process.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
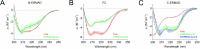



Similar articles
-
Hierarchy of merlin and ezrin N- and C-terminal domain interactions in homo- and heterotypic associations and their relationship to binding of scaffolding proteins EBP50 and E3KARP.J Biol Chem. 2001 Mar 9;276(10):7621-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006708200. Epub 2000 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11106646
-
Characterization of the Ca2+ -regulated ezrin-S100P interaction and its role in tumor cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2008 Oct 24;283(43):29331-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806145200. Epub 2008 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18725408 Free PMC article.
-
Ezrin self-association involves binding of an N-terminal domain to a normally masked C-terminal domain that includes the F-actin binding site.Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Aug;6(8):1061-75. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.8.1061. Mol Biol Cell. 1995. PMID: 7579708 Free PMC article.
-
ERM Proteins at the Crossroad of Leukocyte Polarization, Migration and Intercellular Adhesion.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1502. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041502. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ezrin Mediates Invasion and Metastasis in Tumorigenesis: A Review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 10;8:588801. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.588801. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33240887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Lysine-Rich Delivery Peptides of Plant Origin ERD and Human S100: The Effect of Carboxyfluorescein Conjugation, Influence of Aromatic and Proline Residues, Cellular Internalization, and Penetration Ability.ACS Omega. 2021 Dec 6;6(50):34470-34484. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04637. eCollection 2021 Dec 21. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34963932 Free PMC article.
-
The S100A4 Transcriptional Inhibitor Niclosamide Reduces Pro-Inflammatory and Migratory Phenotypes of Microglia: Implications for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Cells. 2019 Oct 16;8(10):1261. doi: 10.3390/cells8101261. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31623154 Free PMC article.
-
S-Nitrosylation: An Emerging Paradigm of Redox Signaling.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Sep 17;8(9):404. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090404. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31533268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Suppressor p53TAD1-60 Forms a Fuzzy Complex with Metastasis-Associated S100A4: Structural Insights and Dynamics by an NMR/MD Approach.Chembiochem. 2020 Nov 2;21(21):3087-3095. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202000348. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Chembiochem. 2020. PMID: 32511842 Free PMC article.
-
A biophysical perspective of the regulatory mechanisms of ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins.Biophys Rev. 2022 Jan 28;14(1):199-208. doi: 10.1007/s12551-021-00928-0. eCollection 2022 Feb. Biophys Rev. 2022. PMID: 35340609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Neisch AL, Fehon RG. Ezrin, Radixin and Moesin: key regulators of membrane-cortex interactions and signaling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2011;23(4):377–82. Epub 2011/05/20. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3148288. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.04.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clucas J, Valderrama F. ERM proteins in cancer progression. J Cell Sci. 2015;128(6):1253 Epub 2015/03/17. doi: 10.1242/jcs.170027 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barreiro O, Yanez-Mo M, Serrador JM, Montoya MC, Vicente-Manzanares M, Tejedor R, et al. Dynamic interaction of VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 with moesin and ezrin in a novel endothelial docking structure for adherent leukocytes. The Journal of cell biology. 2002;157(7):1233–45. PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2173557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200112126 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Granes F, Urena JM, Rocamora N, Vilaro S. Ezrin links syndecan-2 to the cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 2000;113 (Pt 7):1267–76. - PubMed
-
- Martin TA, Harrison G, Mansel RE, Jiang WG. The role of the CD44/ezrin complex in cancer metastasis. Critical reviews in oncology/hematology. 2003;46(2):165–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

