MiR-338-3p regulates neuronal maturation and suppresses glioblastoma proliferation
- PMID: 28493990
- PMCID: PMC5426787
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177661
MiR-338-3p regulates neuronal maturation and suppresses glioblastoma proliferation
Abstract
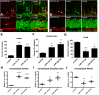
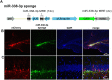
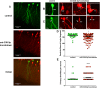
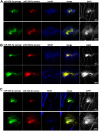
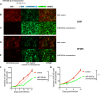
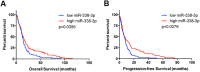
Neurogenesis is a highly-regulated process occurring in the dentate gyrus that has been linked to learning, memory, and antidepressant efficacy. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been previously shown to play an important role in the regulation of neuronal development and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus via modulation of gene expression. However, this mode of regulation is both incompletely described in the literature thus far and highly multifactorial. In this study, we designed sensors and detected relative levels of expression of 10 different miRNAs and found miR-338-3p was most highly expressed in the dentate gyrus. Comparison of miR-338-3p expression with neuronal markers of maturity indicates miR-338-3p is expressed most highly in the mature neuron. We also designed a viral "sponge" to knock down in vivo expression of miR-338-3p. When miR-338-3p is knocked down, neurons sprout multiple primary dendrites that branch off of the soma in a disorganized manner, cellular proliferation is upregulated, and neoplasms form spontaneously in vivo. Additionally, miR-338-3p overexpression in glioblastoma cell lines slows their proliferation in vitro. Further, low miR-338-3p expression is associated with increased mortality and disease progression in patients with glioblastoma. These data identify miR-338-3p as a clinically relevant tumor suppressor in glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-139-3p suppresses growth and metastasis of glioblastoma via inhibition of NIN1/RPNI2 binding protein 1 homolog.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 May;23(10):4264-4274. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201905_17931. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31173298
-
Expression level of miRNAs on chromosome 14q32.31 region correlates with tumor aggressiveness and survival of glioblastoma patients.J Neurooncol. 2016 Dec;130(3):413-422. doi: 10.1007/s11060-016-2248-0. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Neurooncol. 2016. PMID: 27573219
-
Involvement of miRNAs in the differentiation of human glioblastoma multiforme stem-like cells.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 14;8(10):e77098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077098. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24155920 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 in targeting glioblastoma stemness.Cancer Lett. 2014 Oct 10;353(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25042866 Review.
-
miRNA signature in glioblastoma: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Dec;117:104550. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104550. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33010295 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Factor NFAT5 Promotes Glioblastoma Cell-driven Angiogenesis via SBF2-AS1/miR-338-3p-Mediated EGFL7 Expression Change.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Sep 21;10:301. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00301. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28983240 Free PMC article.
-
MiR338-3p expression in extracellular vesicles after severe trauma with or without traumatic brain injury.Brain Commun. 2025 Jun 21;7(4):fcaf242. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaf242. eCollection 2025. Brain Commun. 2025. PMID: 40666703 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA expression profiles in liver grafts of HCV and HIV/HCV-infected recipients, 6 months after liver transplantation.J Med Virol. 2021 Aug;93(8):4992-5000. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26999. Epub 2021 May 4. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33818800 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion in human malignant melanoma by targeting MACC1.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Aug;18(2):997-1004. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7644. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Exp Ther Med. 2019. Retraction in: Exp Ther Med. 2024 Apr 08;27(6):245. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12533. PMID: 31316597 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Diversification of dentate gyrus granule cell subtypes is regulated by Nrg1 nuclear back-signaling.Life Sci Alliance. 2025 Apr 25;8(7):e202403169. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202403169. Print 2025 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2025. PMID: 40280713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, et al. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med. 1998;4(11):1313–7. doi: 10.1038/3305 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aimone JB, Li Y, Lee SW, Clemenson GD, Deng W, Gage FH. Regulation and function of adult neurogenesis: from genes to cognition. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(4):991–1026. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, et al. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science. 2003;301(5634):805–9. doi: 10.1126/science.1083328 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Pandey GN, Dwivedi Y. Hippocampal cell proliferation regulation by repeated stress and antidepressants. Neuroreport. 2006;17(9):863–7. doi: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000221827.03222.70 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

