Correlation Between Dynamic Contour Tonometry, Uncorrected and Corrected Goldmann Applanation Tonometry, and Stage of Glaucoma
- PMID: 28494071
- PMCID: PMC5540028
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.1012
Correlation Between Dynamic Contour Tonometry, Uncorrected and Corrected Goldmann Applanation Tonometry, and Stage of Glaucoma
Abstract
Importance: Accurate determination of intraocular pressure (IOP) is crucial for the diagnosis and management of glaucoma. Objective clinical evaluation of the correction equations for Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT) is lacking.
Objectives: To investigate the difference between corrected and conventional GAT and Pascal dynamic contour tonometry (DCT) measurements, as well as the correlation between discordant IOP values and stage of glaucoma.
Design, setting, and participants: This prospective cross-sectional case series was conducted at the Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Zurich, and Talacker Eye Center between July 1, 2011, and May 31, 2016, among 112 white patients with glaucoma.
Interventions: Intraocular pressure measurements were performed with GAT and DCT in a randomized order. Goldmann applanation tonometry measurements were modified with 5 correction equations.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was degree of concordance between corrected or uncorrected GAT and DCT measurements. The secondary end point was association between discordant IOP measurements and the stage of glaucoma, as assessed by the Glaucoma Severity Score.
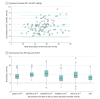
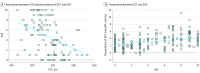
Results: Among the 112 patients (67 women and 45 men; mean [SD] age, 66.3 [13.1] years), 63 of the eyes in the study (56.3%) were left eyes and 85 patients (75.9%) were taking ocular antihypertensive medications. Mean (SD) IOP was 20.3 (4.5) mm Hg (95% CI, 19.4-21.1) as measured by DCT and 17.0 [4.1] mm Hg (95% CI, 16.3-17.8) as measured by GAT. The mean (SD) discordance between DCT and GAT measurements was -3.3 (2.0) mm Hg (95% CI, 2.9-3.6). The 5 corrected GAT values ranged from -2.7 to -5.4 mm Hg compared with DCT. The mean (SD) result of the Dresdner correction formula (17.6 [4.1] mm Hg) was closer to the DCT measurement than the original GAT measurement. The mean (SD) Glaucoma Severity Score was 4.7 (3.4) (95% CI, 4.1-5.4). The uncorrected discordance IOPDCT - IOPGAT showed a positive correlation with the Glaucoma Severity Score (rs = 0.33; P < .001) and a negative correlation with central corneal thickness (rs = -0.22; P = .02).
Conclusions and relevance: In comparison with DCT measurements, these data suggest that GAT values are significantly discordant in eyes with thin corneas and advanced glaucoma. Application of GAT-based correction formulas involves a possible risk of creating an even greater number of unpredictable measurement errors. Hence, we advise with caution, especially pertaining to eyes with thin corneas, to not place reliance on GAT readings, and abandon any correction formula.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT01474070.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Stop "Adjusting" Intraocular Pressure Measurements.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017 Jun 1;135(6):608-609. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.1035. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28494074 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ceruti P, Morbio R, Marraffa M, Marchini G. Comparison of Goldmann applanation tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry in healthy and glaucomatous eyes. Eye (Lond). 2009;23(2):262-269. - PubMed
-
- Kotecha A, White E, Schlottmann PG, Garway-Heath DF. Intraocular pressure measurement precision with the Goldmann applanation, dynamic contour, and ocular response analyzer tonometers. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(4):730-737. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Roberts CJ. Influence of corneal biomechanical properties on intraocular pressure measurement: quantitative analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31(1):146-155. - PubMed
-
- Mark HH. Corneal curvature in applanation tonometry. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973;76(2):223-224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

