MicroRNA-338 modulates cortical neuronal placement and polarity
- PMID: 28494198
- PMCID: PMC5546544
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1325067
MicroRNA-338 modulates cortical neuronal placement and polarity
Abstract
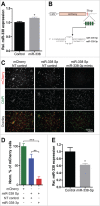
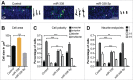
The precise spatial and temporal regulation of gene expression orchestrates the many intricate processes during brain development. In the present study we examined the role of the brain-enriched microRNA-338 (miR-338) during mouse cortical development. Reduction of miR-338 levels in the developing mouse cortex, using a sequence-specific miR-sponge, resulted in a loss of neuronal polarity in the cortical plate and significantly reduced the number of neurons within this cortical layer. Conversely, miR-338 overexpression in developing mouse cortex increased the number of neurons, which exhibited a multipolar morphology. All together, our results raise the possibility for a direct role for this non-coding RNA, which was recently associated with schizophrenia, in the regulation of cortical neuronal polarity and layer placement.
Keywords: Epigenetic gene regulation; in utero electroporation; neurodevelopment; neuronal migration; schizophrenia.
Figures

References
-
- Franco SJ, Muller U. Shaping our minds: stem and progenitor cell diversity in the mammalian neocortex. Neuron 2013; 77:19-34; PMID:23312513; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.12.022 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lui JH, Hansen DV, Kriegstein AR. Development and evolution of the human neocortex. Cell 2011; 146:18-36; PMID:21729779; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.030 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.005 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schubert D, Martens GJ, Kolk SM. Molecular underpinnings of prefrontal cortex development in rodents provide insights into the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2015; 20:795-809; PMID:25450230; https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.147 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Bokhoven H. Genetic and epigenetic networks in intellectual disabilities. Annu Rev Genet 2011; 45:81-104; PMID:21910631; https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-110410-132512 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stark KL, Xu B, Bagchi A, Lai WS, Liu H, Hsu R, Wan X, Pavlidis P, Mills AA, Karayiorgou M, et al.. Altered brain microRNA biogenesis contributes to phenotypic deficits in a 22q11-deletion mouse model. Nat Genet 2008; 40:751-60; PMID:18469815; https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.138 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
