Cisplatin and paclitaxel co-delivered by folate-decorated lipid carriers for the treatment of head and neck cancer
- PMID: 28494629
- PMCID: PMC8241145
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1236849
Cisplatin and paclitaxel co-delivered by folate-decorated lipid carriers for the treatment of head and neck cancer
Abstract
Context: For head and neck cancer therapy, co-delivery of two drugs, cisplatin (DDP) plus paclitaxel (PTX), are more effective than single drug therapy. Lipid carriers are promising drug carriers for anti-cancer delivery.
Objective: The aim of this study is to construct a folate (FA) decorated nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) as nanocarriers for DDP and PTX delivery.
Materials and methods: In this study, DDP and PTX were incorporated into NLCs. Folate-PEG-DSPE (FA-PEG-DSPE) was synthesized and decorated the drugs-loaded NLCs (FA-DDP/PTX NLCs). Their average size, zeta potential, drug encapsulation efficiency, drug loading capacity, and in vitro drug release were evaluated. Head and neck cancer cells (FaDu cells) were used for the testing of in vitro cytotoxicity, and in vivo transfection efficiency of NLC was evaluated on mice bearing FaDu cells model.
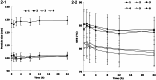
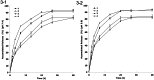
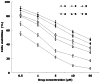
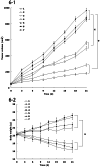
Results: The size of FA-DDP/PTX NLCs was around 127 nm, with a positive zeta potential of 26.7 mV. FA-DDP/PTX NLCs showed the highest cytotoxicity and synergistic effect of two drugs in head and neck cancer cells (FaDu cells) in vitro. The in vivo study revealed the greatest anti-tumor activity than all the other formulations in murine-bearing head and neck cancer model.
Discussion and conclusion: FA-DDP/PTX NLCs effectively improves anticancer efficiency for head and neck cancer in vitro and in vivo. The constructed NLCs could be used as a novel carrier to co-delivery DDP and PTX for head and neck cancer therapy.
Keywords: Cisplatin; co-delivery; head and neck cancer; lipid carriers; paclitaxel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that they have no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
Figures

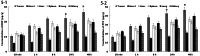
References
-
- Alam MI, Baboota S, Ahuja A, et al. (2013). Intranasal infusion of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) containing CNS acting drug and estimation in brain and blood. Drug Deliv 20:247–51 - PubMed
-
- Bernkop-Schnürch A, Giovanelli R, Valenta C. (2000). Peroral administration of enzymes: strategies to improve the galenic of dosage forms for trypsin and bromelain. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 26:115–21 - PubMed
-
- Ding J, Feng M, Wang F, et al. (2015). Targeting effect of PEGylated liposomes modified with the Arg-Gly-Asp sequence on gastric cancer. Oncol Rep 34:1825–34 - PubMed
-
- Dosio F, Arpicco S, Stella B, et al. (2009). Folate-mediated targeting of albumin conjugates of paclitaxel obtained through a heterogeneous phase system. Int J Pharm 382:117–23 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
