Inhibition of CD40-TRAF6 interactions by the small molecule inhibitor 6877002 reduces neuroinflammation
- PMID: 28494768
- PMCID: PMC5427621
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-017-0875-9
Inhibition of CD40-TRAF6 interactions by the small molecule inhibitor 6877002 reduces neuroinflammation
Abstract
Background: The influx of leukocytes into the central nervous system (CNS) is a key hallmark of the chronic neuro-inflammatory disease multiple sclerosis (MS). Strategies that aim to inhibit leukocyte migration across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) are therefore regarded as promising therapeutic approaches to combat MS. As the CD40L-CD40 dyad signals via TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) in myeloid cells to induce inflammation and leukocyte trafficking, we explored the hypothesis that specific inhibition of CD40-TRAF6 interactions can ameliorate neuro-inflammation.
Methods: Human monocytes were treated with a small molecule inhibitor (SMI) of CD40-TRAF6 interactions (6877002), and migration capacity across human brain endothelial cells was measured. To test the therapeutic potential of the CD40-TRAF6-blocking SMI under neuro-inflammatory conditions in vivo, Lewis rats and C57BL/6J mice were subjected to acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and treated with SMI 6877002 for 6 days (rats) or 3 weeks (mice).
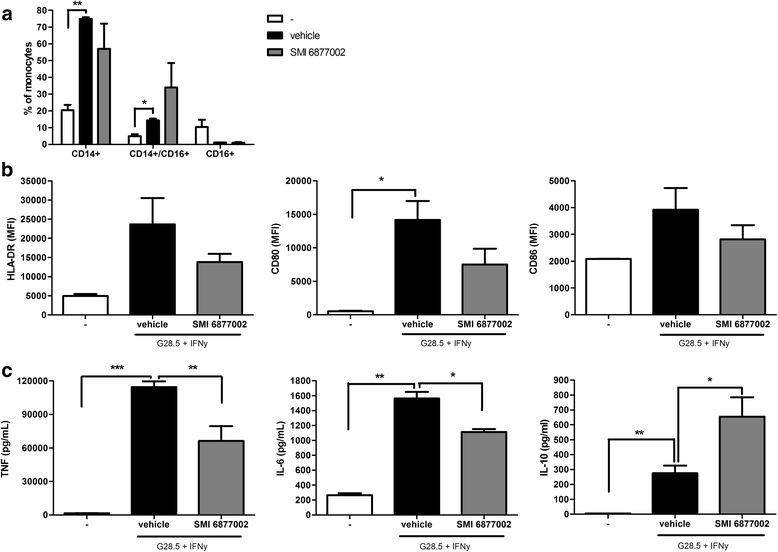
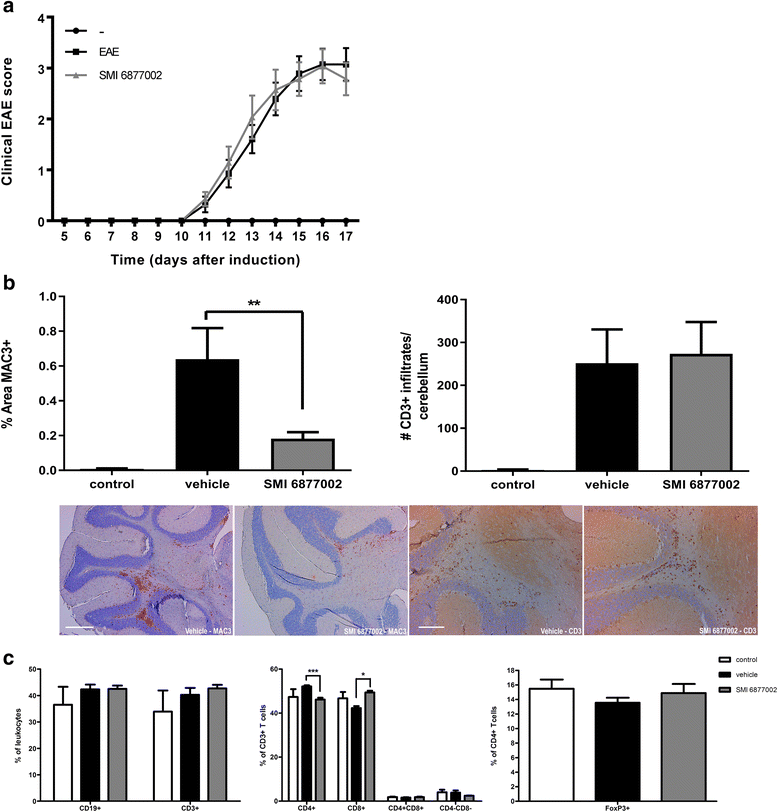
Results: We here show that a SMI of CD40-TRAF6 interactions (6877002) strongly and dose-dependently reduces trans-endothelial migration of human monocytes. Moreover, upon SMI treatment, monocytes displayed a decreased production of ROS, tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and interleukin (IL)-6, whereas the production of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was increased. Disease severity of EAE was reduced upon SMI treatment in rats, but not in mice. However, a significant reduction in monocyte-derived macrophages, but not in T cells, that had infiltrated the CNS was eminent in both models.
Conclusions: Together, our results indicate that SMI-mediated inhibition of the CD40-TRAF6 pathway skews human monocytes towards anti-inflammatory cells with reduced trans-endothelial migration capacity, and is able to reduce CNS-infiltrated monocyte-derived macrophages during neuro-inflammation, but minimally ameliorates EAE disease severity. We therefore conclude that SMI-mediated inhibition of the CD40-TRAF6 pathway may represent a beneficial treatment strategy to reduce monocyte recruitment and macrophage activation in the CNS and has the potential to be used as a co-treatment to combat MS.
Keywords: Co-stimulation; EAE; Inflammation; Monocytes; Multiple sclerosis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Macrophage CD40 signaling drives experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Pathol. 2019 Apr;247(4):471-480. doi: 10.1002/path.5205. Epub 2019 Jan 30. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30471110 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of the adenosine A2a receptor in autoimmune neuroinflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Feb 26;13:48. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0512-z. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 26920550 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate Ameliorates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Inhibiting Leukocyte Migration to the Central Nervous System.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 Aug;22(8):707-14. doi: 10.1111/cns.12561. Epub 2016 May 11. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016. PMID: 27165523 Free PMC article.
-
CD40-TRAF6 inhibition suppresses cardiovascular inflammation, oxidative stress and functional complications in a mouse model of arterial hypertension.Redox Biol. 2025 Mar;80:103520. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103520. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 39899926 Free PMC article.
-
The CD40-CD40L Dyad in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 12;8:1791. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01791. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29312317 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploration of Aberrant E3 Ligases Implicated in Alzheimer's Disease and Development of Chemical Tools to Modulate Their Function.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 18;15:768655. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.768655. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34867205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of TRAF6 in Central Nervous System.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(9):1306-1313. doi: 10.2174/1570159X16666180412094655. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29651950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward Small-Molecule Inhibition of Protein-Protein Interactions: General Aspects and Recent Progress in Targeting Costimulatory and Coinhibitory (Immune Checkpoint) Interactions.Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(8):674-699. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666180531092503. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29848279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of TRAF6 in peripheral blood B cells of patients with myasthenia gravis.BMC Neurol. 2022 Aug 17;22(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02833-9. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35978310 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting CD40-Induced TRAF6 Signaling in Macrophages Reduces Atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Feb 6;71(5):527-542. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.11.055. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29406859 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

