Association between fluid intake and mortality in critically ill patients with negative fluid balance: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 28494815
- PMCID: PMC5427534
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1692-3
Association between fluid intake and mortality in critically ill patients with negative fluid balance: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Compared to positive fluid balance (FB), negative FB is associated with improved clinical outcomes in critically ill patients. However, as to whether achieving more negative FB can further improve outcomes has not been investigated. This study aimed to investigate whether more negative FB and restricted fluid intake were associated with improved outcomes in critically ill patients.
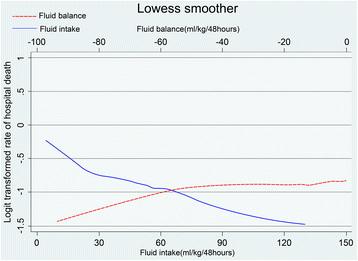
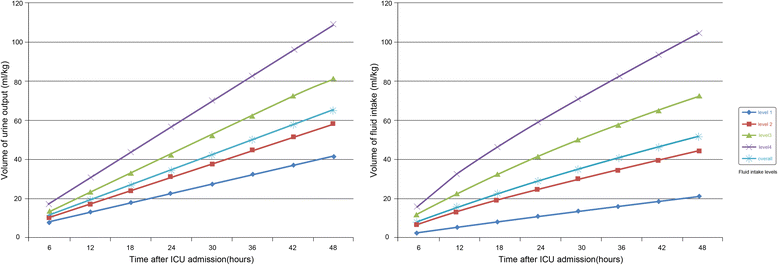
Method: Data were extracted from the Multi-parameter Intelligent Monitoring in Intensive Care III Database. Patients achieving negative FB at 48 hours after intensive care unit (ICU) admission were screened. The primary outcome was hospital mortality. Logistic models were built to explore the association between FB, fluid intake and mortality, using FB and fluid intake (both four levels) as design variables and using the linear spline function method.
Results: There were 2068 patients meeting the inclusion criteria. Compared to slight negative FB (level 1), there was a decreased tendency towards mortality with FB level 2 (OR 0.88, 95% CI 0.69-1.11) and level 3 (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0. 65-1.11); however, only extreme negative FB (level 4) was significant (OR 0.56, 95% CI 0. 33-0.95). Fluid intake and urine output were evenly distributed over the first 48 hours after ICU admission. Fluid intake was inversely associated with hospital mortality, with the OR decreased stepwise from level 2 (OR 0.73, 95% CI 0.56-0.96) to level 4 (OR 0.47, 95% CI 0.30-0.74), referred to level 1. Urine output also showed a similar pattern. Diuretic use was associated with higher mortality in both models.
Conclusion: In critically ill patients with negative FB, both increased fluid intake and urine output were associated with decreased hospital mortality. However, compared to slight FB, achieving more negative FB was not associated with reduced mortality.
Keywords: Critically ill; Diuretics; Fluid intake; Mortality; Negative fluid balance.
Figures
References
-
- Brotfain E, Koyfman L, Toledano R, Borer A, Fucs L, Galante O, Frenkel A, Kutz R, Klein M. Positive fluid balance as a major predictor of clinical outcome of patients with sepsis/septic shock after discharge from intensive care unit. Am J Emerg Med. 2016;34(11):2122–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical