HIV Reprograms Human Airway Basal Stem/Progenitor Cells to Acquire a Tissue-Destructive Phenotype
- PMID: 28494859
- PMCID: PMC5521803
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.026
HIV Reprograms Human Airway Basal Stem/Progenitor Cells to Acquire a Tissue-Destructive Phenotype
Abstract
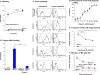
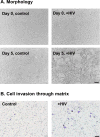
While highly active anti-retroviral therapy has dramatically improved the survival of HIV-infected individuals, there is an increased risk for other co-morbidities, such as COPD, manifesting as emphysema. Given that emphysema originates around the airways and that human airway basal cells (BCs) are adult airway stem/progenitor cells, we hypothesized that HIV reprograms BCs to a distinct phenotype that contributes to the development of emphysema. Our data indicate that HIV binds to but does not replicate in BCs. HIV binding to BCs induces them to acquire an invasive phenotype, mediated by upregulation of MMP-9 expression through activation of MAPK signaling pathways. This HIV-induced "destructive" phenotype may contribute to degradation of extracellular matrix and tissue damage relevant to the development of emphysema commonly seen in HIV+ individuals.
Keywords: HIV; MMP-9; airway basal stem/progenitor cells; matrix metalloproteinase-9; reprogramming.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
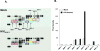


References
-
- Atkinson JJ, Senior RM. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 in lung remodeling. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;28:12–24. - PubMed
-
- Beck JM, Rosen MJ, Peavy HH. Pulmonary complications of HIV infection. Report of the Fourth NHLBI Workshop. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:2120–2126. - PubMed
-
- Beeh KM, Beier J, Kornmann O, Buhl R. Sputum matrix metalloproteinase-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloprotinease-1, and their molar ratio in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and healthy subjects. Respir Med. 2003;97:634–639. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia NS, Chow FC. Neurologic Complications in Treated HIV-1 Infection. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016;16:62. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia R, Ryscavage P, Taiwo B. Accelerated aging and human immunodeficiency virus infection: emerging challenges of growing older in the era of successful antiretroviral therapy. J Neurovirol. 2012;18:247–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

