Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression
- PMID: 28494868
- PMCID: PMC6420824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.031
Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression
Erratum in
-
Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression.Cell Rep. 2019 Dec 10;29(11):3766. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.113. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31825850 No abstract available.
Abstract
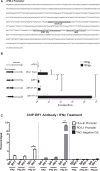
PD-L1 and PD-L2 are ligands for the PD-1 immune inhibiting checkpoint that can be induced in tumors by interferon exposure, leading to immune evasion. This process is important for immunotherapy based on PD-1 blockade. We examined the specific molecules involved in interferon-induced signaling that regulates PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in melanoma cells. These studies revealed that the interferon-gamma-JAK1/JAK2-STAT1/STAT2/STAT3-IRF1 axis primarily regulates PD-L1 expression, with IRF1 binding to its promoter. PD-L2 responded equally to interferon beta and gamma and is regulated through both IRF1 and STAT3, which bind to the PD-L2 promoter. Analysis of biopsy specimens from patients with melanoma confirmed interferon signature enrichment and upregulation of gene targets for STAT1/STAT2/STAT3 and IRF1 in anti-PD-1-responding tumors. Therefore, these studies map the signaling pathway of interferon-gamma-inducible PD-1 ligand expression.
Keywords: IRF1; JAK-STATs; PD-1; PD-L1; PD-L2; immunotherapy; interferon receptor signaling pathways; melanoma.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

