Spatial mapping of humeral head bone density
- PMID: 28495573
- PMCID: PMC5567411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jse.2017.03.006
Spatial mapping of humeral head bone density
Abstract
Background: Short-stem humeral replacements achieve fixation by anchoring to the metaphyseal trabecular bone. Fixing the implant in high-density bone can provide strong fixation and reduce the risk of loosening. However, there is a lack of data mapping the bone density distribution in the proximal humerus. The aim of the study was to investigate the bone density in proximal humerus.
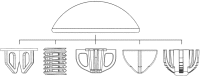
Methods: Eight computed tomography scans of healthy cadaveric humeri were used to map bone density distribution in the humeral head. The proximal humeral head was divided into 12 slices parallel to the humeral anatomic neck. Each slice was then divided into 4 concentric circles. The slices below the anatomic neck, where short-stem implants have their fixation features, were further divided into radial sectors. The average bone density for each of these regions was calculated, and regions of interest were compared using a repeated-measures analysis of variance with significance set at P < .05.
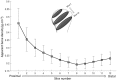
Results: Average apparent bone density was found to decrease from proximal to distal regions, with the majority of higher bone density proximal to the anatomic neck of the humerus (P < .05). Below the anatomic neck, bone density increases from central to peripheral regions, where cortical bone eventually occupies the space (P < .05). In distal slices below the anatomic neck, a higher bone density distribution in the medial calcar region was also observed.
Conclusion: This study indicates that it is advantageous with respect to implant fixation to preserve some bone above the anatomic neck and epiphyseal plate and to use the denser bone at the periphery.
Keywords: Shoulder arthroplasty; humeral bone density; humeral component; implant design; implant fixation; implant loosening; short-stem devices.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Barvencik F., Gebauer M., Beil F.T., Vettorazzi E., Mumme M., Rupprecht M. Age-and sex-related changes of humeral head microarchitecture: histomorphometric analysis of 60 human specimens. J Orthop Res. 2010;28:18–26. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jor.20957 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Churchill R.S. Stemless shoulder arthroplasty: current status. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23:1409–1414. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jse.2014.05.005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Favre P., Seebeck J., Thistlethwaite P.A., Obrist M., Steffens J.G., Hopkins A.R. In vitro initial stability of a stemless humeral implant. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2016;32:113–117. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2015.12.004 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hepp P., Lill H., Bail H., Korner J., Niederhagen M., Haas N.P. Where should implants be anchored in the humeral head? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;415:139–147. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

