Dynamic expression and regulatory mechanism of TGF-β signaling in chicken embryonic stem cells differentiating into spermatogonial stem cells
- PMID: 28495881
- PMCID: PMC6434085
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20170179
Dynamic expression and regulatory mechanism of TGF-β signaling in chicken embryonic stem cells differentiating into spermatogonial stem cells
Abstract
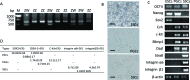
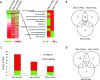
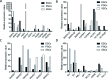
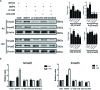
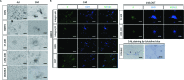
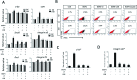
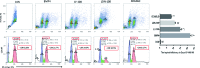
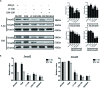
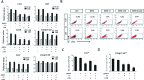
The present study investigated the dynamic expression and regulatory mechanism of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling involved in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) differentiation into male germ cells. Candidate genes involved in TGF-β signaling pathway were screened from RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq), which were further validated by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) was used to induce differentiation of ESCs in vitro Inhibition of TGF-β signaling pathway was reflected by Western blot of SMAD2 and SMAD5 expression. Differentiating efficiency of germ cells was evaluated by immunofluorescence and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). Germ cell marker genes were assessed by qRT-PCR in the differentiation process, with activation or inhibition of TGF-β signaling pathway. In the process of in vitro induction, SMAD2 and SMAD5 were found to significantly up-regulated in BMP4 group versus the control and inhibition groups after 4 and 14 days. Expression of CKIT, CVH, DAZL, STRA8, and INTEGRIN α6 were significantly increased in the BMP4 group compared with the control group, while down-regulated in the inhibition groups. The proportion of germ cell-like cells was decreased from 17.9% to 2.2% after 4 days induction, and further decreased from 14.1% to 2.1% after 14 days induction. Correspondingly, expression of marker genes in germ cells was significantly lower. In vivo inhibition of TGF-β signaling pathway reduced germ cells formation from 5.5% to 1.6%, and down-regulated the expression of CKIT, CVH, DAZL, STRA8, and INTEGRIN α6 In conclusion, our study reveals the mechanism regulating spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs) and lays the basis for further understanding of the regulatory network.
Keywords: Embryonic stem cells; Primordial germ cells; RNA-seq; Spermatogonial stem cells; TGF-β signaling.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
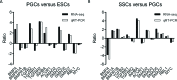
References
-
- Yue J., Mulder K.M., Yue J. and Mulder K.M. (2001) Transforming growth factor-β signal transduction in epithelial cells. Pharmacol. Ther. 91, 1–34 - PubMed
-
- Nohe A., Keating E., Knaus P. and Petersen N.O. (2004) Signal transduction of bone morphogenetic protein receptors. Cell. Signal. 16, 291–299 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

