Association between tea consumption and risk of cognitive disorders: A dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies
- PMID: 28496007
- PMCID: PMC5522147
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17429
Association between tea consumption and risk of cognitive disorders: A dose-response meta-analysis of observational studies
Abstract
Background: The epidemiological evidence for a dose-response relationship between tea consumption and risk of cognitive disorders is sparse. The aim of the study was to summarize the evidence for the association of tea consumption with risk of cognitive disorders and assess the dose-response relationship.
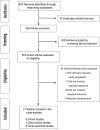
Methods: We searched electronic databases of Pubmed, Embase, and Cochrane Library (from 1965 to Jan 19, 2017) for eligible studies that published in the international journals. A random-effects model was used to pool the most adjusted odds ratios (ORs) and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
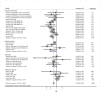
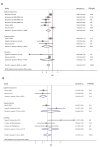
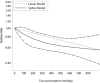
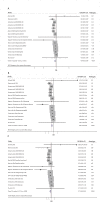
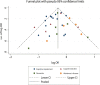
Results: Seventeen studies involving 48,435 participants were included in our study. The meta-analysis showed that a higher tea consumption was associated with a significant reduction in the risk of cognitive disorders (OR=0.73, 95% CI: 0.65-0.82). When considering the specific types of tea consumption, the significantly inverse association is only found in green tea consumption (OR=0.64, 95% CI: 0.53-0.77) but not in black/oolong tea consumption (OR=0.75, 95% CI: 0.55-1.01). Dose-response meta-analysis indicated that tea consumption is linearly associated with a reduced risk of cognitive disorders. An increment of 100 ml/day, 300 ml/day, and 500 ml/day of tea consumption was associated with a 6% (OR=0.94, 95% CI: 0.92-0.96), 19% (OR=0.81, 95% CI: 0.74-0.88), and 29% (OR=0.71, 95% CI: 0.62-0.82) lower risk of cognitive disorders.
Conclusions: Tea consumption is inversely and linearly related to the risk of cognitive disorders. More studies are needed to further confirm our findings.
Keywords: cognitive disorders; dose-response; meta-analysis; tea consumption.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Ritchie K, Touchon J. Mild cognitive impairment: conceptual basis and current nosological status. Lancet. 2000;355:225–228. - PubMed
-
- Prince M, Bryce R, Albanese E, Wimo A, Ribeiro W, Ferri CP. The global prevalence of dementia: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:63–75.e2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

