Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity Correlates with OGG1 in Ozone-Induced Lung Injury Animal Models
- PMID: 28496412
- PMCID: PMC5406453
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00249
Nitric Oxide Synthase Activity Correlates with OGG1 in Ozone-Induced Lung Injury Animal Models
Abstract
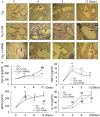
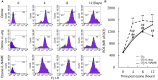
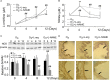
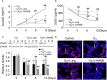
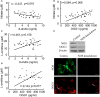
Background: NO is an important cellular signaling molecule which is derived from L-arginine by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and the effects of NOS signaling in lung injury is conflicting. The present study was designed to observe the effect of NOS and Arginase signaling in the occurrence and development of lung injury and its mechanism. Methods: An ozone-stressed lung injury animal model was established by exposure to 2.0 ppm O3 for 30 min every day for consecutive 12 day with or without the administration of NO precursor L-arginine or non-selective NOS inhibitor N-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME). Then, the lung histopathology, the releases of inflammatory mediators and the production of ROS were assayed by immunohistochemistry, ELISA and flow cytometry respectively. The activities and expression of NOS and Arginase were assayed by biochemical methods and western blot. Correspondingly, the release of 8-oxoguanine glycosylase 1(8-OxoG) and 8-oxoguanine glycosylase 1 (OGG1) were assayed by ELISA and western blot. The correlation between NOS/Arginase signaling with 8-OxoG/ OGG1 was also analyzed by Pearson correlation coefficients and immunofluorescence in NOS deficient bronchial epithelial cells. Results: In ozone-induced rat lung injury models, lung inflammation as well as lung architecture was disrupted in a time dependent manner. Ozone treatment with L-arginine showed a substantial attenuation of adverse lung histopathological changes and treatment with L-NAME promoted the inflammation and remodeling. Importantly, the expression of NOS was promoted by L-arginine and inhibited by L-NAME and the expression of Arginase was promoted by L-NAME treatment. Further, we observed significantly higher levels of 8-OxoG and lower levels of OGG1 in ozone group which was reversed by L-arginine and promoted by L-NAME. The expression of NOS is closely related with 8-OxoG /OCG1. Conclusion: These findings give further evidence that the NOS signaling is related with base excise repair.
Keywords: 8-OxoG; NOS; OGG1; arginase; lung injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of intrinsic cavernous tone and nitric oxide production by arginase in rabbit corpus cavernosum.J Urol. 2004 Jan;171(1):490-4. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000088343.68746.65. J Urol. 2004. PMID: 14665961
-
Beneficial effects of high dose of L-arginine on airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Mar;125(3):626-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.065. Epub 2010 Feb 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20153031
-
L-arginine uptake and metabolism by lung macrophages and neutrophils following intratracheal instillation of silica in vivo.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998 Aug;19(2):308-15. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.19.2.2814. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9698604
-
Nitric oxide synthase inhibition and oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases: possible therapeutic targets?Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Dec;140(3):239-57. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23859953 Review.
-
An active alternative splicing isoform of human mitochondrial 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (OGG1).Genes Environ. 2015 Oct 1;37:21. doi: 10.1186/s41021-015-0021-9. eCollection 2015. Genes Environ. 2015. PMID: 27350816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of DNA repair enzyme OGG1 in innate immunity and its significance for lung cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Feb;194:59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30240635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule-mediated OGG1 inhibition attenuates pulmonary inflammation and lung fibrosis in a murine lung fibrosis model.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 6;14(1):643. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36314-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36746968 Free PMC article.
-
Role and Mechanism of Maresin-1 in Acute Lung Injury Induced by Trauma-Hemorrhagic Shock.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Aug 4;26:e923518. doi: 10.12659/MSM.923518. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32750045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai R., Guan L., Zhang W., Xu J., Rui W., Zhang F., et al. . (2016). Comparative study of the effects of PM1-induced oxidative stress on autophagy and surfactant protein B and C expressions in lung alveolar type II epithelial MLE-12 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1860, 2782–2792. 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.05.020 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

