Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of Celexocib Using Tris-(2-hydroxyethyl) Ammonium Acetate as an Efficient and Reusable Catalyst
- PMID: 28496471
- PMCID: PMC5423243
Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of Celexocib Using Tris-(2-hydroxyethyl) Ammonium Acetate as an Efficient and Reusable Catalyst
Abstract
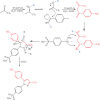
Celecoxib is classified as none traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This compound has conventional properties of NSAIDs such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic activities beside reduced risk of gastrointestinal side effect of traditional NSAIDs such as ibuprofen. This compound gets a second sale rank of NSAIDs market at 2016 in the world and sales more than 17000 Kg in Iran during the past 6 month. So, a simple, rapid and green method for synthesis of this compound is important. In the present study, a novel green method was suggested for the synthesis of celecoxib using the ionic liquid. Celecoxib was provided by the reaction of trifluoroacetone, 4-methylbenzoylchloride, and 4-hydrazinobenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride. The tris-(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium acetate as ionic liquid was prepared by mixing tris-(2-hydroxyethyl) ammonium and acetic acid, and used as an efficient catalyst. The structure of the synthetic products was confirmed by analytical and spectroscopic methods including 1HNMR, 13CNMR, IR, MS and elemental analysis. This ionic liquid can play dual roles in the synthesis of celecoxib, as a catalyst to improve electrophilicity of carbonyl group and also as a solvent of reaction. The reaction rate and yield (86%) were improved considerably. Moreover IL showed the same efficiency when used in 4 consecutive reactions.
Keywords: 4-hydrazinobenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride; 4-methylbenzoylchloride; Anti-inflammatory agent; Celecoxib; Ionic liquid; Trifluoroacetone.
Figures

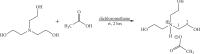


References
-
- Sandilands EA, Bateman DN. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicine . 2016;44:185–6.
-
- Theodosis-Nobelos P, Kourti M, Gavalas A, Rekka EA. Amides of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with thiomorpholine can yield hypolipidemic agents with improved anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. . 2016;26:910–3. - PubMed
-
- Schönthal AH, Chen TC, Hofman FM, Louie SG, Petasis NA. Celecoxib analogs that lack COX-2 inhibitory function: preclinical development of novel anticancer drugs. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs . 2008;17:197–208. - PubMed
-
- Habeeb AG, Praveen Rao PN, Knaus EE. Design and Synthesis of Celecoxib and Rofecoxib Analogues as Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Inhibitors: Replacement of Sulfonamide and Methylsulfonyl Pharmacophores by an Azido Bioisostere. J. Med. Chem. . 2001;44:3039–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
