Cytotoxic Properties of Three Isolated Coumarin-hemiterpene Ether Derivatives from Artemisia armeniaca Lam
- PMID: 28496477
- PMCID: PMC5423249
Cytotoxic Properties of Three Isolated Coumarin-hemiterpene Ether Derivatives from Artemisia armeniaca Lam
Abstract
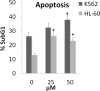
Considering multiple reports on cytotoxic activity of the Artemisia genus and its phytochemicals, in the current study A. armeniaca Lam. and the three components isolated from the plant were subjected to cytotoxic studies. Analytical fractionation of A. armeniaca aerial parts for the first time was directed to the isolation of 7-hydroxy-8-(4-hydroxy-3-methylbutoxy) comarin (armenin), 8-hydroxy-7-(4-hydroxy-3-methylbutoxy) comarin (isoarmenin) and deoxylacarol. Cytotoxicity assessed with alamalBlue® assay and apoptosis was detected by PI staining and western blot analysis of Bax and PARP proteins. Extracts and all compounds exhibited cytotoxic activity against apoptosis-proficient HL-60 and apoptosis-resistant K562 cells, with the lowest cytotoxic activity on J774 cell line as non-malignant cell. Armenin as the most potent component decreased the viability of cell with IC50 of 22.5 and 71.1 µM for K562 and HL-60 cells respectively and selected for further mechanistic study. Armenin increased the sub-G1 peak in flow cytometry histogram of HL-60 and K562 treated cells and increase in the amount of Bax protein and the cleavage of PARP in comparison with the control after treatment for 48 h in K562 treated cells verified the apoptotic activity of the armenin. Taken together, according to the finding of this study armenin was introduced as a novel cytotoxic compound with apoptotic activity, which is encouraging for further mechanistic and clinical studies.
Keywords: Artemisia armeniaca; Asteraceae leukemic cell lines; apoptosis; coumarin-hemiterpene ether derivatives.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Armenin and isoarmenin--two prenylated coumarins from the aerial parts of Artemisia armeniaca.Chem Biodivers. 2011 Nov;8(11):2097-103. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201000284. Chem Biodivers. 2011. PMID: 22083921
-
Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of extracts of Artemisia ciniformis Krasch. and Popov ex Poljakov on K562 and HL-60 cell lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(17):7055-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.17.7055. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25227790
-
Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of different extracts of Artemisia biennis Willd. on K562 and HL-60 cell lines.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017 Feb;20(2):166-171. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2017.8242. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28293393 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of different extracts of Artemisia turanica Krasch. on K562 and HL-60 cell lines.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Oct 28;2013:628073. doi: 10.1155/2013/628073. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24288497 Free PMC article.
-
New coumarin-hemiterpene ether glucosides and a structurally related phenylpropanoic acid derivative from Artemisia armeniaca.Nat Prod Commun. 2010 Oct;5(10):1619-22. Nat Prod Commun. 2010. PMID: 21121260
Cited by
-
Coumarins and Coumarin-Related Compounds in Pharmacotherapy of Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 19;12(7):1959. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071959. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32707666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiangiogenic Effects of Coumarins against Cancer: From Chemistry to Medicine.Molecules. 2019 Nov 24;24(23):4278. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234278. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31771270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Analysis and Various Biological Activities of the Aerial Parts of Scrophularia Atropatana Growing in Iran.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Summer;18(3):1543-1555. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.1100782. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 32641962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Narang AS, Desai DS. Anticancer Drug Development Unique Aspects of Pharmaceutical Development. In: Lu Y, Mahato RI, editors. Pharmaceutical Perspectives of Cancer Therapeutics. Springer Science+Business Media; 2009. pp. 49–93.
-
- Kong AN, Yu R, Chen C, Mandlekar S, Primiano T. Signal transduction events elicited by natural products: role of MAPK and caspase pathways in homeostatic response and induction of apoptosis. Arch. Pharm. Res. . 2000;23:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian V. A Dictionary of Iranian Plant Names. Tehran: Farhang Moaser Publishers; 1998. pp. 56–8.
-
- Rybalko KS, Konovalova OA, Sheichenko VI, Zakharov PI. Armenin a new coumarin from Artemisia armeniaca. Khim. Prir. Soed. . 1976;3:294–8.
-
- Szabo G, Greger H, Hofer O. Coumarin-hemiterpene ethers from Artemisia species. Phytochemistry . 1985;24:537–41.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
