Homoisoflavonoids and the Antioxidant Activity of Ophiopogon japonicus Root
- PMID: 28496489
- PMCID: PMC5423261
Homoisoflavonoids and the Antioxidant Activity of Ophiopogon japonicus Root
Abstract
The root of Ophiopogon japonicus has been used as a traditional Chinese medicine and also a functional food ingredient for a long time in China. In the present study, 17 different homoisoflavonoid compounds were identified in the root extract of O. japonicus by HPLC-DAD and LCMS/MS analyses. The antioxidant activity of the of chloroform/methanol (1:1, v/v), methanol and 70% ethanol extracts, and two major isolated homoisoflavonoid compounds (methylophiopogonanone A and methylophiopogonanone B) from O. japonicus root were investigated by various in-vitro assays. Methylophiopogonanone B showed the highest antioxidant ability according to four antioxidant methods. Among the extracts, the chloroform/methanol extract which contained high amounts of homoisoflavonoids was found to exhibit the strongest antioxidant activity. The results showed that O. japonicus root can be regarded as a potential source of homoisoflavonoids and natural antioxidant.
Keywords: Antioxidant activity; Homoisoflavonoids; LCMS/MS analysis; Ophiopogon japonicas.
Figures
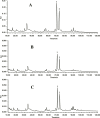
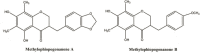
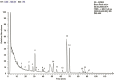
References
-
- Li N, Zhang L, Zeng KW, Zhou Y, Zhang JY, Che YY, Tu PF. Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from Ophiopogon japonicus. Steroids . 2013;78:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Choi SB, Wha JD, Park SM. The insulin sensitizing effect of homoisoflavone-enriched fraction in Liriope platyphylla Wang et Tang via PI3-kinase pathway. Life Sci. . 2004;75:2653–2664. - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Zhang Z, Lin X, Xu DS, Feng Y, Ding K. A polysaccharide, MDG-1, induces S1P1 and bFGF expression and augments survival and angiogenesis in the ischemic heart. Glycobiology . 2010;20:473–484. - PubMed
-
- Ma C, Li G, Zhang J, Zheng Q, Fan X, Wang Z. An efficient combination of supercritical fluid extraction and high-speed counter-current chromatography to extract and purify homoisoflavonoids from Ophiopogon japonicus (Thunb) Ker-Gawler. J. Sep. Sci. . 2009;32:1949–1956. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
