Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
- PMID: 28496688
- PMCID: PMC5152997
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.287
Atrial Fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome
Abstract
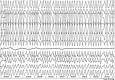
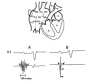
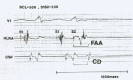
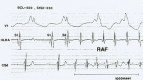
Since the advent of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF) aiming the pulmonary veins a few years ago, there has been an overwhelming interest and a dramatic increase in AF investigation. AF has a different dimension in the context of the Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome. Indeed, AF may be a nightmare in a young person that has an accessory pathway (AP) with fast anterograde conduction. It may be life-threatening if an extremely rapid ventricular response develops degenerating into ventricular fibrillation. Therefore, it is very important to know the mechanisms involved in the development of AF in the WPW syndrome. There are several possible mechanisms that may be involved in the development of AF in the WPW syndrome, namely, spontaneous degeneration of atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia into AF, the electrophysiological properties of the AP, the effects of AP on atrial architecture, and intrinsic atrial muscle vulnerability. Focal activity, multiple reentrant wavelets, and macroreentry have all been implicated in AF, perhaps under the further influence of the autonomic nervous system. AF can also be initiated by ectopic beats originating from the pulmonary veins, and elsewhere. Several studies demonstrated a decrease incidence of AF after successful elimination of the AP, suggesting that the AP itself may play an important role in the initiation of AF. However, since AF still occurs in some patients with the WPW syndrome even after successful ablation of the AP, there should be other mechanisms responsible for the development of AF in the WPW syndrome. There is a clear evidence of an underlying atrial muscle disease in patients with the WPW syndrome. Atrial myocardial vulnerability has been studied performing an atrial endocardial catheter mapping during sinus rhythm, and analizing the recorded abnormal atrial electrograms. This review analizes the available data on this singular setting since AF has a reserved prognostic significance in patients with the WPW syndrome, and has an unusually high incidence in the absence of any clinical evidence of organic heart disease.
Figures

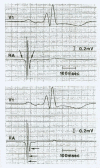
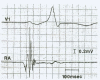
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms for the genesis of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in the Wolff Parkinson-White syndrome: intrinsic atrial muscle vulnerability vs. electrophysiological properties of the accessory pathway.Europace. 2008 Mar;10(3):294-302. doi: 10.1093/europace/eun031. Europace. 2008. PMID: 18308751 Review.
-
Mechanisms for atrial fibrillation in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002 Mar;13(3):223-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1540-8167.2002.00223.x. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11942586
-
Evaluation of atrial vulnerability immediately after radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory pathway in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2009 Dec;26(3):217-24. doi: 10.1007/s10840-009-9438-z. Epub 2009 Oct 21. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19844784 Clinical Trial.
-
Risk factors for atrioventricular tachycardia degenerating to atrial flutter/fibrillation in the young with Wolff-Parkinson-White.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008 Oct;31(10):1307-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8159.2008.01182.x. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18811812
-
Pre-Excited Atrial Fibrillation in Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome: A Case Report and a Review of the Literature.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Mar 29;25(4):125. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2504125. eCollection 2024 Apr. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39076547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pre-excited atrial fibrillation revealed at a very delayed age: case report.Int J Emerg Med. 2023 May 11;16(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12245-023-00506-z. Int J Emerg Med. 2023. PMID: 37170212 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Detection of Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome Using the Atrioventricular Interval on Fetal Echocardiogram.CJC Pediatr Congenit Heart Dis. 2024 Sep 20;4(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cjcpc.2024.09.003. eCollection 2025 Feb. CJC Pediatr Congenit Heart Dis. 2024. PMID: 40170989 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of a Mechanism-Based Ventricular Electrical Storm Management.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 29;14(15):5351. doi: 10.3390/jcm14155351. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40806975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: De novo variants and evidence for mutational burden in genes associated with atrial fibrillation.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Jun;182(6):1387-1399. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61571. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 32233023 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, Management, and Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation in Paediatric Patients: Insights from a Tertiary Cardiology Centre.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Sep 15;60(9):1505. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091505. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Khan Fakhar Z, Dutka David Paul, Fynn Simon Patrick. Recorded spontaneous sudden cardiac arrest in a patient with pre-excited atrial fibrillation. Europace. 2009 Jan;11 (1) - PubMed
-
- Schwieler Jonas H, Zlochiver Sharon, Pandit Sandeep V, Berenfeld Omer, Jalife José, Bergfeldt Lennart. Reentry in an accessory atrioventricular pathway as a trigger for atrial fibrillation initiation in manifest Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome: a matter of reflection? Heart Rhythm. 2008 Sep;5 (9):1238–47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barold S Serge. Malignant atrial fibrillation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Cardiol J. 2007;14 (1):95–6. - PubMed
-
- Thanavaro Joanne L, Thanavaro Samer. Clinical presentation and treatment of atrial fibrillation in Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Heart Lung. 2010 Mar 9;39 (2):131–6. - PubMed
-
- Shapira Adam R. Catheter ablation of supraventricular arrhythmias and atrial fibrillation. Am Fam Physician. 2009 Nov 15;80 (10):1089–94. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
