Respiratory Cycle-Dependent Atrial Trachycardia; its Unique Characteristics and Relation with Autonomic Nerve System
- PMID: 28496788
- PMCID: PMC5153152
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.570
Respiratory Cycle-Dependent Atrial Trachycardia; its Unique Characteristics and Relation with Autonomic Nerve System
Abstract
Respiration influences the sinus heart rate, however, little is still known about the tachyarrhythmias related to respiration. Atrial tachycardia (AT) rarely emerges during inspiration and it also ceases during expiration. This type of AT is thus called respiratory cycle-dependent atrial tachycardia (RCAT), and it demonstrates a centrifugal activation pattern. Based on these peculiar P wave morphologies, the foci converged either around the right superior pulmonary vein (RSPV) or inside the superior vena cava where the anterior right ganglionated plexi (ARGP) is considered to be located. The mechanism of such AT is therefore thought to be related to the activity of the autonomic system.
Figures
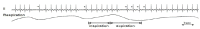
Similar articles
-
Respiratory cycle-dependent atrial tachycardia: prevalence, electrocardiographic and electrophysiologic characteristics, and outcome after catheter ablation.Heart Rhythm. 2011 Oct;8(10):1615-21. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2011.04.031. Epub 2011 May 4. Heart Rhythm. 2011. PMID: 21699840
-
Ganglionated plexi modulate extrinsic cardiac autonomic nerve input: effects on sinus rate, atrioventricular conduction, refractoriness, and inducibility of atrial fibrillation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007 Jul 3;50(1):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.02.066. Epub 2007 Jun 18. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17601547
-
Gradients of atrial refractoriness and inducibility of atrial fibrillation due to stimulation of ganglionated plexi.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007 Jan;18(1):83-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2006.00679.x. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17229305
-
Ganglionated plexi as neuromodulation targets for atrial fibrillation.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017 Dec;28(12):1485-1491. doi: 10.1111/jce.13319. Epub 2017 Sep 8. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28833764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the Atrial Neural Plexis a Therapeutic Target in Atrial Fibrillation?Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2015 Apr-Jun;11(2):82-6. doi: 10.14797/mdcj-11-2-82. Methodist Debakey Cardiovasc J. 2015. PMID: 26306124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Melcher A. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in man. A study in heart rate regulating mechanisms. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1976;435 ():1–31. - PubMed
-
- OKADA H. REFLEX RESPONSES TO STIMULATION OF BARORECEPTORS IN THE RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY. Am. J. Physiol. 1964 Apr;206 ():918–22. - PubMed
-
- Levy M N, DeGeest H, Zieske H. Effects of respiratory center activity on the heart. Circ. Res. 1966 Jan;18 (1):67–78. - PubMed
-
- Takatsuki S, Mitamura H, Miyoshi S, Ogawa S. Respiratory cycle-dependent left atrial tachycardia. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2001 Oct;12 (10) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
