Role of Intracardiac echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
- PMID: 28496830
- PMCID: PMC5153176
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.786
Role of Intracardiac echocardiography in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
Abstract
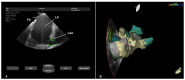
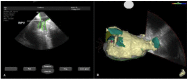
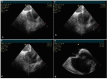
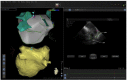
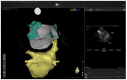
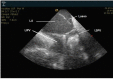
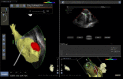
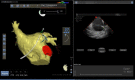
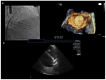
In the recent years, several new evidences support catheter-based ablation as a treatment modality of atrial fibrillation (AF). Based on a plenty of different applications, intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) is now a well-established technology in complex electrophysiological procedures, in particular in AF ablation. ICE contributes to improve the efficacy and safety of such procedures defining the anatomical structures involved in ablation procedures and monitoring in real time possible complications. In particular ICE allows: a correct identification of the endocardial structures; a guidance of transseptal puncture; an assessment of accurate placement of the circular mapping catheter; an indirect evaluation of evolving lesions during radiofrequency (RF) energy delivery via visualization of micro and macrobubbles tissue heating; assessment of catheter contact with cardiac tissues. Recently, also the feasibility of the integration of electroanatomical mapping (EAM) and intracardiac echocardiography has been demonstrated, combining accurate real time anatomical information with electroanatomical data. As a matter of fact, different techniques and ablation strategies have been developed throughout the years. In the setting of balloon-based ablation systems, recently adopted by an increasing number of centers, ICE might have a role in the choice of appropriate balloon size and to confirm accurate occlusion of pulmonary veins. Furthermore, in the era of minimally fluoroscopic ablation, ICE has successfully provided a contribute in reducing fluoroscopy time. The purpose of this review is to summarize the current applications of ICE in catheter based ablation strategies of atrial fibrillation, focusing-on electronically phased-array ICE.
Figures






References
-
- Calkins Hugh, Kuck Karl Heinz, Cappato Riccardo, Brugada Josep, Camm A John, Chen Shih-Ann, Crijns Harry J G, Damiano Ralph J, Davies D Wyn, DiMarco John, Edgerton James, Ellenbogen Kenneth, Ezekowitz Michael D, Haines David E, Haissaguerre Michel, Hindricks Gerhard, Iesaka Yoshito, Jackman Warren, Jalife José, Jais Pierre, Kalman Jonathan, Keane David, Kim Young-Hoon, Kirchhof Paulus, Klein George, Kottkamp Hans, Kumagai Koichiro, Lindsay Bruce D, Mansour Moussa, Marchlinski Francis E, McCarthy Patrick M, Mont J Lluis, Morady Fred, Nademanee Koonlawee, Nakagawa Hiroshi, Natale Andrea, Nattel Stanley, Packer Douglas L, Pappone Carlo, Prystowsky Eric, Raviele Antonio, Reddy Vivek, Ruskin Jeremy N, Shemin Richard J, Tsao Hsuan-Ming, Wilber David. 2012 HRS/EHRA/ECAS expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design: a report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology Foundation, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Heart Rhythm. 2012 Apr;9 (4):632–696.e21. - PubMed
-
- Wilber David J, Pappone Carlo, Neuzil Petr, De Paola Angelo, Marchlinski Frank, Natale Andrea, Macle Laurent, Daoud Emile G, Calkins Hugh, Hall Burr, Reddy Vivek, Augello Giuseppe, Reynolds Matthew R, Vinekar Chandan, Liu Christine Y, Berry Scott M, Berry Donald A. Comparison of antiarrhythmic drug therapy and radiofrequency catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2010 Jan 27;303 (4):333–40. - PubMed
-
- Wazni Oussama M, Marrouche Nassir F, Martin David O, Verma Atul, Bhargava Mandeep, Saliba Walid, Bash Dianna, Schweikert Robert, Brachmann Johannes, Gunther Jens, Gutleben Klaus, Pisano Ennio, Potenza Dominico, Fanelli Raffaele, Raviele Antonio, Themistoclakis Sakis, Rossillo Antonio, Bonso Aldo, Natale Andrea. Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2005 Jun 01;293 (21):2634–40. - PubMed
-
- Pappone Carlo, Augello Giuseppe, Sala Simone, Gugliotta Filippo, Vicedomini Gabriele, Gulletta Simone, Paglino Gabriele, Mazzone Patrizio, Sora Nicoleta, Greiss Isabelle, Santagostino Andreina, LiVolsi Laura, Pappone Nicola, Radinovic Andrea, Manguso Francesco, Santinelli Vincenzo. A randomized trial of circumferential pulmonary vein ablation versus antiarrhythmic drug therapy in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the APAF Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006 Dec 05;48 (11):2340–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
