Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Focus on Treatment Options
- PMID: 28496929
- PMCID: PMC5368549
- DOI: 10.4022/jafib.1450
Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: Focus on Treatment Options
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is leading cardiac arrhythmia with important clinical implications. Its diagnosis is usually made on the basis on 12-lead ECG or 24-hour Holter monitoring. More and more clinical evidence supports diagnostic use of cardiac event recorders and cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIED). Treatment options in patients with atrial fibrillation are extensive and are based on chosen rhythm and/or rate control strategy. The use and selected contraindications to AF related pharmacotherapy, including anticoagulants are shown. Nonpharmacological treatments, comorbidities and risk factors control remain mainstay in the treatment of patients with AF. Electrical cardioversion consists important choice in rhythm control strategy. Much progress has been made in the field of catheter ablation and cardiac surgery methods. Left atrial appendage occlusion/closure may be beneficial in patients with AF. CIED are used with clinical benefits in both, rhythm and rate control. Pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators and cardiac resynchronization therapy devices with different pacing modes have guaranteed place in the treatment of patients with AF. On the other hand, the concepts of permanent leadless cardiac pacing, atrial dyssynchrony syndrome treatment and His-bundle or para-Hisian pacing have been proposed. This review summarizes and discusses current and novel treatment options in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Keywords: Ablation; Atrial Fibrillation; CRT; ICD; Pacemaker; Treatment.
Figures

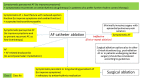
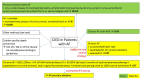
References
-
- Chugh Sumeet S, Havmoeller Rasmus, Narayanan Kumar, Singh David, Rienstra Michiel, Benjamin Emelia J, Gillum Richard F, Kim Young-Hoon, McAnulty John H, Zheng Zhi-Jie, Forouzanfar Mohammad H, Naghavi Mohsen, Mensah George A, Ezzati Majid, Murray Christopher J L. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation. 2014 Feb 25;129 (8):837–47. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kristensen Marie S, Zwisler Ann-Dorthe, Berg Selina K, Zangger Graziella, Grønset Charlotte N, Risom Signe S, Pedersen Susanne S, Oldridge Neil, Thygesen Lau C. Validating the HeartQoL questionnaire in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2016 Sep;23 (14):1496–503. - PubMed
-
- Emdin Connor A, Wong Christopher X, Hsiao Allan J, Altman Douglas G, Peters Sanne Ae, Woodward Mark, Odutayo Ayodele A. Atrial fibrillation as risk factor for cardiovascular disease and death in women compared with men: systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMJ. 2016 Jan 19;532 () - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dewland Thomas A, Vittinghoff Eric, Mandyam Mala C, Heckbert Susan R, Siscovick David S, Stein Phyllis K, Psaty Bruce M, Sotoodehnia Nona, Gottdiener John S, Marcus Gregory M. Atrial ectopy as a predictor of incident atrial fibrillation: a cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013 Dec 03;159 (11):721–8. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stein Phyllis K. Increased randomness of heart rate could explain increased heart rate variability preceding onset of atrial fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004 Aug 04;44 (3):668–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
