The Transcription Regulator Krüppel-Like Factor 4 and Its Dual Roles of Oncogene in Glioblastoma and Tumor Suppressor in Neuroblastoma
- PMID: 28497005
- PMCID: PMC5423539
- DOI: 10.1615/ForumImmunDisTher.2016017227
The Transcription Regulator Krüppel-Like Factor 4 and Its Dual Roles of Oncogene in Glioblastoma and Tumor Suppressor in Neuroblastoma
Abstract
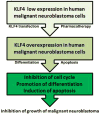
The Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) gene is located on chromosome 9q31. All of the currently known 17 KLF transcription regulators that have similarity with members of the specificity protein family are distinctly characterized by the Cys2/His2 zinc finger motifs at their carboxyl terminals for preferential binding to the GC/GT box or the CACCC element of the gene promoter and enhancer regions. KLF4 is a transcriptional regulator of cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion, emphasizing its importance in diagnosis and prognosis of particular tumors. KLF4 has been implicated in tumor progression as well as in tumor suppression, depending on tumor types and contexts. Different studies so far strongly suggest that KLF4 acts as an oncogene in glioblastoma, which is the most malignant and prevalent brain tumor in human adult. It is now well established that the presence of glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) in glioblastoma causes therapy resistance and progressive growth of the tumor. Because KLF4 is one of the key stemness factors in GSCs, it is likely that KLF4 contributes significantly to the survival of GSCs and the recurrence of glioblastoma. On the other hand, recent studies show that KLF4 can act as a tumor suppressor in human malignant neuroblastoma, which is a deadly tumor mostly in children, by inhibiting the cell cycle and activating the cell differentiation and death pathways. Our increasing understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the contrasting roles of KLF4 in glioblastoma and neuroblastoma is useful for superior diagnosis, therapy, and prognosis of these tumors of the nervous system.
Keywords: KLF4; glioblastoma; neuroblastoma; oncogene; tumor suppressor.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
