Impact of polyethylene glycol 400/propylene glycol/hydroxypropyl-guar and 0.1% sodium hyaluronate on postoperative discomfort following cataract extraction surgery: a comparative study
- PMID: 28497070
- PMCID: PMC5424421
- DOI: 10.1186/s40662-017-0079-5
Impact of polyethylene glycol 400/propylene glycol/hydroxypropyl-guar and 0.1% sodium hyaluronate on postoperative discomfort following cataract extraction surgery: a comparative study
Abstract
Background: Universal postoperative guidelines for cataract extraction surgery are yet to be introduced. Artificial tears are gaining popularity as an additional integral component of the postoperative regime. The primary objective of this study was to explore the impact of two prevalent artificial tear preparations on postoperative discomfort following cataract extraction surgery.
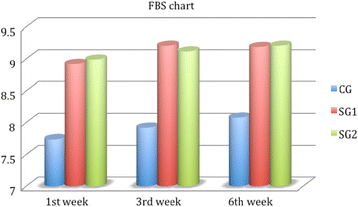
Methods: A total of 180 patients that underwent cataract extraction surgery were randomly divided into three groups according to their postoperative regime: a) Study group 1 (SG1) received a fixed combination of tobramycin and dexamethasone (FCTD) quid for 3 weeks and, additionally polyethylene glycol 400/propylene glycol/hydroxypropyl-guar quid, for 6 weeks, b) Study group 2 (SG2) received FCTD quid for 3 weeks and, additionally 0.1% sodium hyaluronate provided in the COMOD® device quid, for 6 weeks, and, c) Control Group (CG) received only FCTD quid for 3 weeks. The following indexes were evaluated at three postoperative checkpoints: 1) Subjective discomfort index (SDI) derived from four direct 10-scale Likert-type questions that were addressed to the patient and pertained to: a) foreign body sensation (FBS), b) blinking discomfort (BD), c) stinging sensation (SS), d) tearing sensation (TS), 2) Tear break-up time (TBUT), 3) Central corneal thickness (CCT) and, 4) Central Corneal Sensitivity (CCS).
Results: Both groups showed increased CCT values at the first examination point and reduced CCS values at all examination points. Furthermore, both SGs had better TBUT times at all examination points compared to CG (CG: 8.86 ± 1.08, SG1: 9.59 ± 1.45, CG2: 9.45 ± 1.33, p < 0.05). BD was significantly better in both SGs only at the 1st week of examination, while SDI values were better until the 3rd week and only borderline better at 6th week. Lastly, no significant differences were detected between SGs, regarding all parameters, at all examination points.
Conclusion: Polyethylene glycol 400/propylene glycol/hydroxypropyl-guar and 0.1% sodium hyaluronate provided in the COMOD® device seem to be equally efficient in alleviating OSD symptoms following cataract extraction surgery and any of them should be routinely added to the postoperative regime.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02558218NCT02558218.
Keywords: Artificial tears; Cataract; Hylocomod; Postoperative regimen; Surface discomfort index; Systane.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous