Efficient Production of Papillomavirus Gene Delivery Vectors in Defined In Vitro Reactions
- PMID: 28497074
- PMCID: PMC5423317
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtm.2017.04.005
Efficient Production of Papillomavirus Gene Delivery Vectors in Defined In Vitro Reactions
Abstract
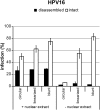
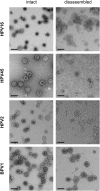
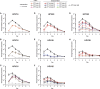
Papillomavirus capsids can package a wide variety of nonviral DNA plasmids and deliver the packaged genetic material to cells, making them attractive candidates for targeted gene delivery vehicles. However, the papillomavirus vectors generated by current methods are unlikely to be suitable for clinical applications. We have developed a chemically defined, cell-free, papillomavirus-based vector production system that allows the incorporation of purified plasmid DNA (pseudogenome) into high-titer papillomavirus L1/L2 capsids. We investigated the incorporation of several DNA forms into a variety of different papillomavirus types, including human and animal types. Our results show that papillomavirus capsids can package and transduce linear or circular DNA under defined conditions. Packaging and transduction efficiencies were surprisingly variable across capsid types, DNA forms, and assembly reaction conditions. The pseudoviruses produced by these methods are sensitive to the same entry inhibitors as cell-derived pseudovirions, including neutralizing antibodies and heparin. The papillomavirus vector production systems developed in this study generated as high as 1011 infectious units/mg of L1. The pseudoviruses were infectious both in vitro and in vivo and should be compatible with good manufacturing practice (GMP) requirements.
Keywords: gene delivery; gene packaging; papillomavirus.
Figures



References
-
- Guan J., Bywaters S.M., Brendle S.A., Ashley R.E., Makhov A.M., Conway J.F., Christensen N.D., Hafenstein S. Cryoelectron microscopy maps of human papillomavirus 16 reveal L2 densities and heparin binding site. Structure. 2016;25:253–263. - PubMed
-
- Ishii Y., Ozaki S., Tanaka K., Kanda T. Human papillomavirus 16 minor capsid protein L2 helps capsomeres assemble independently of intercapsomeric disulfide bonding. Virus Genes. 2005;31:321–328. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

