Structural heterogeneity in the intrinsically disordered RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain
- PMID: 28497792
- PMCID: PMC5437306
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15231
Structural heterogeneity in the intrinsically disordered RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain
Abstract
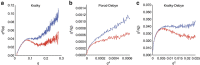
RNA polymerase II contains a repetitive, intrinsically disordered, C-terminal domain (CTD) composed of heptads of the consensus sequence YSPTSPS. The CTD is heavily phosphorylated and serves as a scaffold, interacting with factors involved in transcription initiation, elongation and termination, RNA processing and chromatin modification. Despite being a nexus of eukaryotic gene regulation, the structure of the CTD and the structural implications of phosphorylation are poorly understood. Here we present a biophysical and biochemical interrogation of the structure of the full length CTD of Drosophila melanogaster, which we conclude is a compact random coil. Surprisingly, we find that the repetitive CTD is structurally heterogeneous. Phosphorylation causes increases in radius, protein accessibility and stiffness, without disrupting local structural heterogeneity. Additionally, we show the human CTD is also structurally heterogeneous and able to substitute for the D. melanogaster CTD in supporting fly development to adulthood. This finding implicates conserved structural organization, not a precise array of heptad motifs, as important to CTD function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural determinants for accurate dephosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by its cognate C-terminal domain (CTD) phosphatase during eukaryotic transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 May 24;294(21):8592-8605. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007697. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30971428 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation modulates secondary structure of intrinsically disorder regions in RNA polymerase II.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):108533. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108533. Epub 2025 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40273986 Free PMC article.
-
The C-Terminal Domain of RNA Polymerase II Is a Multivalent Targeting Sequence that Supports Drosophila Development with Only Consensus Heptads.Mol Cell. 2019 Mar 21;73(6):1232-1242.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30765194 Free PMC article.
-
A structural perspective of CTD function.Genes Dev. 2005 Jun 15;19(12):1401-15. doi: 10.1101/gad.1318105. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15964991 Review.
-
RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain with multiple connections.Exp Mol Med. 2007 Jun 30;39(3):247-54. doi: 10.1038/emm.2007.28. Exp Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17603278 Review.
Cited by
-
Rules of Physical Mathematics Govern Intrinsically Disordered Proteins.Annu Rev Biophys. 2022 May 9;51:355-376. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-120221-095357. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Annu Rev Biophys. 2022. PMID: 35119946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A combinatorial view of old and new RNA polymerase II modifications.Transcription. 2020 Apr;11(2):66-82. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2020.1762468. Epub 2020 May 13. Transcription. 2020. PMID: 32401151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Driving forces behind phase separation of the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 25;14(1):5979. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41633-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37749095 Free PMC article.
-
Ovule identity mediated by pre-mRNA processing in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2018 Jan 12;14(1):e1007182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007182. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29329291 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay of in vitro Phosphorylated RNA Polymerase II Carboxyl-terminal Domain Substrates.Bio Protoc. 2020 Jun 20;10(12):e3648. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3648. eCollection 2020 Jun 20. Bio Protoc. 2020. PMID: 33659319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chapman R. D., Heidemann M., Hintermair C. & Eick D. Molecular evolution of the RNA polymerase II CTD. Trends Genet. 24, 289–296 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Eick D. & Geyer M. The RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) code. Chem. Rev. 113, 8456–8490 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Meinhart A. & Cramer P. Recognition of RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain by 3′-RNA-processing factors. Nature 430, 223–226 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Cagas P. M. & Corden J. L. Structural studies of a synthetic peptide derived from the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Proteins 21, 149–160 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

