Nutrients Turned into Toxins: Microbiota Modulation of Nutrient Properties in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 28498348
- PMCID: PMC5452219
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9050489
Nutrients Turned into Toxins: Microbiota Modulation of Nutrient Properties in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
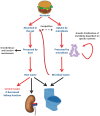
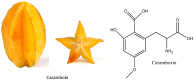
In chronic kidney disease (CKD), accumulation of uremic toxins is associated with an increased risk of death. Some uremic toxins are ingested with the diet, such as phosphate and star fruit-derived caramboxin. Others result from nutrient processing by gut microbiota, yielding precursors of uremic toxins or uremic toxins themselves. These nutrients include l-carnitine, choline/phosphatidylcholine, tryptophan and tyrosine, which are also sold over-the-counter as nutritional supplements. Physicians and patients alike should be aware that, in CKD patients, the use of these supplements may lead to potentially toxic effects. Unfortunately, most patients with CKD are not aware of their condition. Some of the dietary components may modify the gut microbiota, increasing the number of bacteria that process them to yield uremic toxins, such as trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO), p-cresyl sulfate, indoxyl sulfate and indole-3 acetic acid. Circulating levels of nutrient-derived uremic toxins are associated to increased risk of death and cardiovascular disease and there is evidence that this association may be causal. Future developments may include maneuvers to modify gut processing or absorption of these nutrients or derivatives to improve CKD patient outcomes.
Keywords: caramboxin; carnitine; choline; chronic kidney disease; gut–kidney axis; indoxyl sulfate; microbiota; p-cresyl sulfate; trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO); tryptophan; tyrosine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- United States Renal Data System, 2014 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. [(accessed on 20 April 2017)]; Available online: https://iths.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/us-renal-data-system-2014....
-
- Stevens L.A., Li S., Wang C., Huang C., Becker B.N., Bomback A.S., Brown W.W., Burrows N.R., Jurkovitz C.T., McFarlane S.I., et al. Prevalence of CKD and comorbid illness in elderly patients in the United States: Results from the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010;55:S23–S33. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.09.035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ortiz A., Covic A., Fliser D., Fouque D., Goldsmith D., Kanbay M., Mallamaci F., Massy Z.A., Rossignol P., Vanholder R., et al. Epidemiology, contributors to, and clinical trials of mortality risk in chronic kidney failure. Lancet. 2014;383:1831–1843. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60384-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

