Autocrine expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor ligand heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in cervical cancer
- PMID: 28498437
- PMCID: PMC5435322
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3980
Autocrine expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor ligand heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in cervical cancer
Abstract
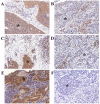
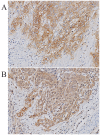
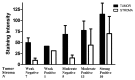
In cervical cancer, the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in 70-90% of the cases and has been associated with poor prognosis. EGFR-based therapy is currently being explored in cervical cancer. We investigated which EGFR ligand is primarily expressed in cervical cancer and which cell type functions as the major source of this ligand. We hypothesized that macrophages are the main source of EGFR ligands and that a paracrine loop between tumor cells and macrophages is responsible for ligand expression. mRNA expression analysis was performed on 32 cervical cancer cases to determine the expression of the EGFR ligands amphiregulin, β-cellulin, epidermal growth factor (EGF), epiregulin, heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB‑EGF) and transforming growth factor α (TGFα). Subsequently, protein expression was determined immunohistochemically on 36 additional cases. To assess whether macrophages are the major source of EGFR ligands, immunohistochemical double staining was performed on four representative tissue slides. Expression of the chemokines granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and C-C motif ligand 2 (CCL2) was determined by mRNA in situ hybridization. Of the known EGFR ligands, HB‑EGF had the highest mRNA expression and HB‑EGF and EGFR protein expression were highly correlated. Tumor specimens with high EGFR expression showed higher numbers of macrophages, and higher expression of GM-CSF and CCL2, but only a small subset (9%) of macrophages was found to be HB‑EGF-positive. Strikingly, 78% of cervical cancer specimens were found to express HB‑EGF. Standardized assessment of staining intensity, using spectral imaging analysis, showed that HB‑EGF expression was higher in the tumor compartment than in the stromal compartment. These results suggest that HB‑EGF is an important EGFR ligand in cervical cancer and that cervical cancer cells are the predominant source of HB‑EGF. Therefore, we propose an autocrine EGFR stimulation model in cervical carcinomas.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Autocrine HBEGF expression promotes breast cancer intravasation, metastasis and macrophage-independent invasion in vivo.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 17;33(29):3784-93. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.363. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24013225 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-ligand based molecular staging predicts prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma partly due to deregulated EGF- induced amphiregulin expression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Sep 26;35(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0422-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27669890 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha in human non-small cell lung cancers.J Formos Med Assoc. 1997 Aug;96(8):579-85. J Formos Med Assoc. 1997. PMID: 9290266
-
EGF receptor ligands: recent advances.F1000Res. 2016 Sep 8;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-2270. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.9025.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27635238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2014 Jan;79:34-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pharmacol Res. 2014. PMID: 24269963 Review.
Cited by
-
The Multiple Functions of HB-EGF in Female Reproduction and Related Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Targeting Strategies.Reprod Sci. 2024 Sep;31(9):2588-2603. doi: 10.1007/s43032-024-01454-6. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Reprod Sci. 2024. PMID: 38424408 Review.
-
Design, synthesis and anti-cancer activity of novel 1,2,3-triazole hybrids of erlotinib against cervical cancer via MAPK signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 9;15(1):24582. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09168-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40628949 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A promising mainstay in targeted cancer therapy.Med Drug Discov. 2024 Sep;23:100195. doi: 10.1016/j.medidd.2024.100195. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Med Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39281823 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling Pathways Cooperate To Mediate Chlamydia Pathogenesis.Infect Immun. 2020 Mar 23;88(4):e00819-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00819-19. Print 2020 Mar 23. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 31964750 Free PMC article.
-
HB-EGF-EGFR Signaling in Bone Marrow Endothelial Cells Mediates Angiogenesis Associated with Multiple Myeloma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 10;12(1):173. doi: 10.3390/cancers12010173. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Joura EA, Ault KA, Bosch FX, Brown D, Cuzick J, Ferris D, Garland SM, Giuliano AR, Hernandez-Avila M, Huh W, et al. Attribution of 12 high-risk human papillomavirus genotypes to infection and cervical disease. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23:1997–2008. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0410. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

