Sequencing of bulks of segregants allows dissection of genetic control of amylose content in rice
- PMID: 28499072
- PMCID: PMC5785344
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.12752
Sequencing of bulks of segregants allows dissection of genetic control of amylose content in rice
Abstract
Amylose content (AC) is a key quality trait in rice. A cross between Oryza glaberrima (African rice) and Oryza sativa (Asian rice) segregating for AC was analysed by sequencing bulks of individuals with high and low AC. SNP associated with the granule bound starch synthase (GBSS1) locus on chromosome 6 were polymorphic between the bulks. In particular, a G/A SNP that would result in an Asp to Asn mutation was identified. This amino acid substitution may be responsible for differences in GBSS activity as it is adjacent to a disulphide linkage conserved in all grass GBSS proteins. Other polymorphisms in genomic regions closely surrounding this variation may be the result of linkage drag. In addition to the variant in the starch biosynthesis gene, SNP on chromosomes 1 and 11 linked to AC was also identified. SNP was found in the genes encoding the NAC and CCAAT-HAP5 transcription factors that have previously been linked to starch biosynthesis. This study has demonstrated that the approach of sequencing bulks was able to identify genes on different chromosomes associated with this complex trait.
Keywords: allele frequency; amylose content; bulk segregant analysis; genetic linkage; genetic markers; whole genome sequencing.
© 2017 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


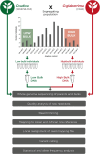
References
-
- Aluko, G. , Martinez, C. , Tohme, J. , Castano, C. , Bergman, C. and Oard, J.H. (2004) QTL mapping of grain quality traits from the interspecific cross Oryza sativa × O. glaberrima . Theor. Appl. Genet. 109, 630–639. - PubMed
-
- Aoki, K. , Ogata, Y. and Shibata, D. (2007) Approaches for Extracting Practical Information from Gene Co‐expression Networks in Plant Biology. Plant Cell Physiol. 48, 381–390. - PubMed
-
- Ayres, N. , McClung, A. , Larkin, P.D. , Bligh, H.F.J. , Jones, C.A. and Park, W.D. (1997) Microsatellites and a single nucleotide polymorphism differentiate apparent amylose classes in an extended pedigree of US rice germplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 94, 773–781.
-
- Bao, J.S. , Corke, H. and Sun, M. (2006) Nucleotide diversity in starch synthase IIa and validation of single nucleotide polymorphisms in relation to starch gelatinization temperature and other physicochemical properties in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 113, 1171–1183. - PubMed
-
- Baxter, G. , Blanchard, C. and Zhao, J. (2014) Effects of glutelin and globulin on the physicochemical properties of rice starch and flour. J. Cereal Sci. 60, 414–420.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

