Ultrastructural deposits appearing as "zebra bodies" in renal biopsy: Fabry disease?- comparative case reports
- PMID: 28499424
- PMCID: PMC5427530
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0571-0
Ultrastructural deposits appearing as "zebra bodies" in renal biopsy: Fabry disease?- comparative case reports
Abstract
Background: Fabry Disease (FD) is a genetic disorder caused by alpha-galactosidase A deficiency. Certain drugs, such as hydroxychloroquine, can produce renal deposits that mimic morphological findings seen in FD, characterizing a type of drug-induced renal phospholipidosis.
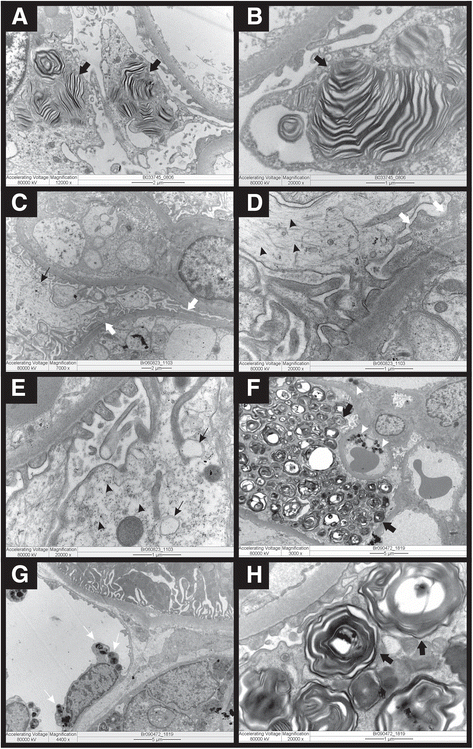
Case presentation: Case 1: A 28-year-old female patient with systemic lupus erythematosus who had been using hydroxychloroquine for 14 months presented subnephrotic proteinuria. Renal biopsy showed deposits compatible with FD. Neither activity analysis of alpha-galactosidase A nor genetic analysis were available and were not performed. These deposits were not detected in a subsequent renal biopsy three years after withdrawal of the medication, characterizing a possible hydroxychloroquine-induced renal phospholipidosis. Case 2: A 29-year-old male patient presented with acroparesthesia, angiokeratomas, cornea verticillata and subnephrotic proteinuria. Deposits compatible with FD were detected upon renal biopsy. The evaluation of alpha-galactosidase A showed no activity in both blood and leukocytes. Genetic analysis identified an M284 T mutation in exon 6, and such mutation was also found in other family members.
Conclusion: Clinical investigation is necessary in suspected cases of Fabry Disease upon renal biopsy in order to confirm diagnosis. Drug-induced renal phospholipidosis should be considered in differential diagnosis in cases with intracellular osmiophilic, lamellar inclusions in electron microscopy.
Keywords: Fabry Disease; Hydroxychloroquine; Lysosomal Storage Disorder; Renal Biopsy; Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Double Hit of Hydroxichloroquine and Amiodarone Induced Renal Phospholipidosis in a Patient with Monoclonal Gammopathy and Sclerodermiform Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Med Sci (Basel). 2024 May 15;12(2):25. doi: 10.3390/medsci12020025. Med Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38804381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zebra Bodies in the Kidney: Is it a Pathognomonic Finding of Fabry Disease?Indian J Nephrol. 2025 Mar-Apr;35(2):298-301. doi: 10.25259/ijn_392_23. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Indian J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40060053 Free PMC article.
-
A possible case of carbamazepine-induced renal phospholipidosis mimicking Fabry disease.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022 Mar;26(3):303-304. doi: 10.1007/s10157-021-02172-y. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35059891
-
[Fabry nephropathy in a female with superposed IgA glomerulonephritis].G Ital Nefrol. 2005 Jul-Aug;22(4):385-9. G Ital Nefrol. 2005. PMID: 16267800 Italian.
-
Renal involvement in Anderson-Fabry disease.J Nephrol. 2003 Mar-Apr;16(2):310-3. J Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 12774774 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabry disease pain: patient and preclinical parallels.Pain. 2021 May 1;162(5):1305-1321. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002152. Pain. 2021. PMID: 33259456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Manifestations of Fabry Disease: A Narrative Review.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2021 Jan 19;8:2054358120985627. doi: 10.1177/2054358120985627. eCollection 2021. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 33786192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic toxicity of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine: prevalence, mechanisms, risk factors, prognostic and screening possibilities.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Jul;41(7):1189-1202. doi: 10.1007/s00296-021-04868-6. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 33893862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does administration of hydroxychloroquine/amiodarone accelerate accumulation of globotriaosylceramide and globotriaosylsphingosine in Fabry mice?Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021 May 29;28:100773. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2021.100773. eCollection 2021 Sep. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021. PMID: 34136356 Free PMC article.
-
Double Hit of Hydroxichloroquine and Amiodarone Induced Renal Phospholipidosis in a Patient with Monoclonal Gammopathy and Sclerodermiform Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Med Sci (Basel). 2024 May 15;12(2):25. doi: 10.3390/medsci12020025. Med Sci (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38804381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Branton M, Schiffmann R, Kopp J. Natural history and treatment of renal involvement in Fabry Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:139–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

