Ca2+ Release Channels Join the 'Resolution Revolution'
- PMID: 28499500
- PMCID: PMC5875148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.04.005
Ca2+ Release Channels Join the 'Resolution Revolution'
Abstract
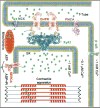
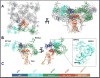
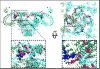
Ryanodine receptors (RyRs) are calcium release channels expressed in the sarcoendoplasmic reticula of many cell types including cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. In recent years Ca2+ leak through RyRs has been implicated as a major contributor to the development of diseases including heart failure, muscle myopathies, Alzheimer's disease, and diabetes, making it an important therapeutic target. Recent mammalian RyR1 cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of multiple functional states have clarified longstanding questions including the architecture of the transmembrane (TM) pore and cytoplasmic domains, the location and architecture of the channel gate, ligand-binding sites, and the gating mechanism. As we advance toward complete models of RyRs this new information enables the determination of domain-domain interfaces and the location and structural effects of disease-causing RyR mutations.
Keywords: calcium channel; cryo-EM; excitation–contraction coupling; ryanodine receptors; structure.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
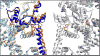
Similar articles
-
Structural Details of the Ryanodine Receptor Calcium Release Channel and Its Gating Mechanism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;981:179-204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55858-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29594862 Review.
-
Structures of the colossal RyR1 calcium release channel.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016 Aug;39:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2016. PMID: 27687475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory mechanisms of ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channel revealed by recent advancements in structural studies.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2021 Jun;42(2):291-304. doi: 10.1007/s10974-020-09575-6. Epub 2020 Feb 10. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2021. PMID: 32040690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward decrypting the allosteric mechanism of the ryanodine receptor based on coarse-grained structural and dynamic modeling.Proteins. 2015 Dec;83(12):2307-18. doi: 10.1002/prot.24951. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Proteins. 2015. PMID: 26492335
-
The Central domain of RyR1 is the transducer for long-range allosteric gating of channel opening.Cell Res. 2016 Sep;26(9):995-1006. doi: 10.1038/cr.2016.89. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 27468892 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Crystal structure of diamondback moth ryanodine receptor Repeat34 domain reveals insect-specific phosphorylation sites.BMC Biol. 2019 Oct 9;17(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12915-019-0698-5. BMC Biol. 2019. PMID: 31597572 Free PMC article.
-
Speg interactions that regulate the stability of excitation-contraction coupling protein complexes in triads and dyads.Commun Biol. 2023 Sep 14;6(1):942. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05330-y. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37709832 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid environment of membrane proteins in cryo-EM based structural analysis.Biophys Rev. 2018 Apr;10(2):307-316. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0371-6. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29256118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis for gating of cardiac ryanodine receptor explains the mechanisms for gain- and loss-of function mutations.Nat Commun. 2022 May 20;13(1):2821. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30429-x. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35595836 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin improves heart preservation through inhibiting hypoxia-dependent L-type calcium channels in cardiomyocytes.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Mar;17(3):2161-2171. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7214. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30867703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rebbeck RT, et al. Skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling: who are the dancing partners? The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology. 2014;48:28–38. - PubMed
-
- Rossi D, Sorrentino V. Molecular genetics of ryanodine receptors Ca2+- release channels. Cell calcium. 2002;32:307–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

