JAK2 inhibitors for myeloproliferative neoplasms: what is next?
- PMID: 28500170
- PMCID: PMC5510786
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-04-742288
JAK2 inhibitors for myeloproliferative neoplasms: what is next?
Abstract
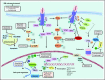
Since its approval in 2011, the Janus kinase 1/2 (JAK1/2) inhibitor ruxolitinib has evolved to become the centerpiece of therapy for myelofibrosis (MF), and its use in patients with hydroxyurea resistant or intolerant polycythemia vera (PV) is steadily increasing. Several other JAK2 inhibitors have entered clinical testing, but none have been approved and many have been discontinued. Importantly, the activity of these agents is not restricted to patients with JAK2 V617F or exon 12 mutations. Although JAK2 inhibitors provide substantial clinical benefit, their disease-modifying activity is limited, and rational combinations with other targeted agents are needed, particularly in MF, in which survival is short. Many such combinations are being explored, as are other novel agents, some of which could successfully be combined with JAK2 inhibitors in the future. In addition, new JAK2 inhibitors with the potential for less myelosuppression continue to be investigated. Given the proven safety and efficacy of ruxolitinib, it is likely that ruxolitinib-based combinations will be a major way forward in drug development for MF. If approved, less myelosuppressive JAK2 inhibitors such as pacritinib or NS-018 could prove to be very useful additions to the therapeutic armamentarium in MF. In PV, inhibitors of histone deacetylases and human double minute 2 have activity, but their role, if any, in the future treatment algorithm is uncertain, given the availability of ruxolitinib and renewed interest in interferons. Ruxolitinib is in late-phase clinical trials in essential thrombocythemia, in which it could fill an important void for patients with troublesome symptoms.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. . Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005;365(9464):1054-1061. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, et al. . A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 2005;434(7037):1144-1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. . A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med 2005;352(17):1779-1790. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. . Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 2005;7(4):387-397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

