Modulation of Kv 11.1 (hERG) channels by 5-(((1H-indazol-5-yl)oxy)methyl)-N-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine (ITP-2), a novel small molecule activator
- PMID: 28500657
- PMCID: PMC5513870
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13859
Modulation of Kv 11.1 (hERG) channels by 5-(((1H-indazol-5-yl)oxy)methyl)-N-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine (ITP-2), a novel small molecule activator
Abstract
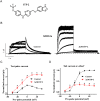
Background and purpose: Activators of Kv 11.1 (hERG) channels have potential utility in the treatment of acquired and congenital long QT (LQT) syndrome. Here, we describe a new hERG channel activator, 5-(((1H-indazol-5-yl)oxy)methyl)-N-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine (ITP-2), with a chemical structure distinct from previously reported compounds.
Experimental approach: Conventional electrophysiological methods were used to assess the effects of ITP-2 on hERG1a and hERG1a/1b channels expressed heterologously in HEK-293 cells.
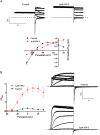
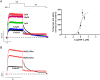
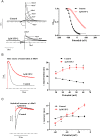
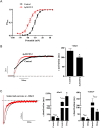
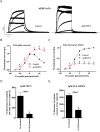
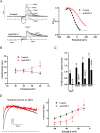
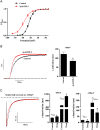
Key results: ITP-2 selectively increased test pulse currents (EC50 1.0 μM) and decreased tail currents. ITP-2 activated hERG1a homomeric channels primarily by causing large depolarizing shifts in the midpoint of voltage-dependent inactivation and hyperpolarizing shifts in the voltage-dependence of activation. In addition, ITP-2 slowed rates of inactivation and made recovery from inactivation faster. hERG1a/1b heteromeric channels showed reduced sensitivity to ITP-2 and their inactivation properties were differentially modulated. Effects on midpoint of voltage-dependent inactivation and rates of inactivation were less pronounced for hERG1a/1b channels. Effects on voltage-dependent activation and activation kinetics were not different from hERG1a channels. Interestingly, hERG1b channels were inhibited by ITP-2. Inactivation-impairing mutations abolished activation by ITP-2 and led to inhibition of hERG channels. ITP-2 exerted agonistic effect from extracellular side of the membrane and could activate one of the arrhythmia-associated trafficking-deficient LQT2 mutants.
Conclusions and implications: ITP-2 may serve as another novel lead molecule for designing robust activators of hERG channels. hERG1a/1b gating kinetics were differentially modulated by ITP-2 leading to altered sensitivity. ITP-2 is capable of activating an LQT2 mutant and may be potentially useful in the development of LQT2 therapeutics.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures



Comment in
-
Modulation of hERG potassium channels by a novel small molecule activator.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;174(20):3669-3671. doi: 10.1111/bph.13964. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28887817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
hERG1a/1b heteromeric currents exhibit amplified attenuation of inactivation in variant 1 short QT syndrome.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Aug 14;386(1):111-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.134. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19501051 Free PMC article.
-
hERG1a and hERG1b potassium channel subunits directly interact and preferentially form heteromeric channels.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 29;292(52):21548-21557. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.816488. Epub 2017 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29089383 Free PMC article.
-
hERG1a N-terminal eag domain-containing polypeptides regulate homomeric hERG1b and heteromeric hERG1a/hERG1b channels: a possible mechanism for long QT syndrome.J Gen Physiol. 2011 Dec;138(6):581-92. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201110683. J Gen Physiol. 2011. PMID: 22124116 Free PMC article.
-
Gating and assembly of heteromeric hERG1a/1b channels underlying I(Kr) in the heart.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;266:4-15; discussion 15-8, 44-5. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16050259 Review.
-
Voltage sensor movement in the hERG K+ channel.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;266:46-52; discussion 52-6, 95-9. doi: 10.1002/047002142x.ch5. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16050261 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac hERG K+ Channel as Safety and Pharmacological Target.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;267:139-166. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_455. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33829343
-
Modulation of hERG potassium channels by a novel small molecule activator.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;174(20):3669-3671. doi: 10.1111/bph.13964. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28887817 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Intracellular Binding of Terfenadine Competes with Its Access to Pancreatic ß-cell ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels and Human ether-à-go-go-Related Gene Channels.J Membr Biol. 2023 Feb;256(1):63-77. doi: 10.1007/s00232-022-00252-y. Epub 2022 Jun 28. J Membr Biol. 2023. PMID: 35763054 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological activation of the hERG K+ channel for the management of the long QT syndrome: A review.J Arrhythm. 2022 Jun 14;38(4):554-569. doi: 10.1002/joa3.12741. eCollection 2022 Aug. J Arrhythm. 2022. PMID: 35936037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson CL, Delisle BP, Anson BD, Kilby JA, Will ML, Tester DJ et al. (2006). Most LQT2 mutations reduce Kv11.1 (hERG) current by a class 2 (trafficking‐deficient) mechanism. Circulation 113: 365–373. - PubMed
-
- Casis O, Olesen SP, Sanguinetti MC (2006). Mechanism of action of a novel human ether‐a‐go‐go‐related gene channel activator. Mol Pharmacol 69: 658–665. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

