Osr1 functions downstream of Hedgehog pathway to regulate foregut development
- PMID: 28501478
- PMCID: PMC5519324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.05.005
Osr1 functions downstream of Hedgehog pathway to regulate foregut development
Abstract
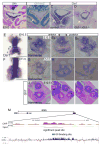
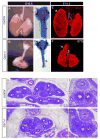
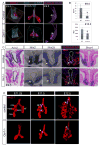
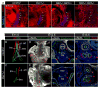
During early fetal development, paracrine Hedgehog (HH) ligands secreted from the foregut epithelium activate Gli transcription factors in the surrounding mesenchyme to coordinate formation of the respiratory system, digestive track and the cardiovascular network. Although disruptions to this process can lead to devastating congenital defects, the underlying mechanisms and downstream targets, are poorly understood. We show that the zinc finger transcription factor Osr1 is a novel HH target as Osr1 expression in the foregut mesenchyme depends on HH signaling and the effector of HH pathway Gli3 binds to a conserved genomic loci near Osr1 promoter region. Molecular analysis of mouse germline Osr1 mutants reveals multiple functions of Osr1 during foregut development. Osr1 mutants exhibit fewer lung progenitors in the ventral foregut. Osr is then required for the proper branching of the primary lung buds, with mutants exhibiting miss-located lung lobes. Finally, Osr1 is essential for proper mesenchymal differentiation including pulmonary arteries, esophageal and tracheal smooth muscle as well as tracheal cartilage rings. Tissue specific conditional knockouts in combination with lineage tracing indicate that Osr1 is required cell autonomously in the foregut mesenchyme. We conclude that Osr1 is a novel downstream target of HH pathway, required for lung specification, branching morphogenesis and foregut mesenchymal differentiation.
Keywords: Esophagus; Hedgehog; Lobulation; Lung; Mesenchyme; Odd-skipped; Specification; Trachea.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
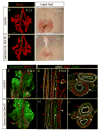
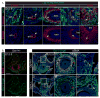
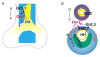
Similar articles
-
Suppression of Bmp4 signaling by the zinc-finger repressors Osr1 and Osr2 is required for Wnt/β-catenin-mediated lung specification in Xenopus.Development. 2012 Aug;139(16):3010-20. doi: 10.1242/dev.078220. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Development. 2012. PMID: 22791896 Free PMC article.
-
Essential function of Gli2 and Gli3 in the formation of lung, trachea and oesophagus.Nat Genet. 1998 Sep;20(1):54-7. doi: 10.1038/1711. Nat Genet. 1998. PMID: 9731531
-
Expression of SHH signaling pathway components in the developing human lung.Histochem Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;134(4):327-35. doi: 10.1007/s00418-010-0738-2. Epub 2010 Sep 7. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20821230
-
Sonic hedgehog regulates branching morphogenesis in the mammalian lung.Curr Biol. 1998 Sep 24;8(19):1083-6. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)70446-4. Curr Biol. 1998. PMID: 9768363 Review.
-
Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into diverse organ-specific mesenchyme of the digestive and respiratory systems.Nat Protoc. 2022 Nov;17(11):2699-2719. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00733-3. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35978039 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The conserved microRNA-229 family controls low-insulin signaling and dietary restriction induced longevity through interactions with SKN-1/NRF2.Aging Cell. 2023 Apr;22(4):e13785. doi: 10.1111/acel.13785. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 36748780 Free PMC article.
-
Building and Regenerating the Lung Cell by Cell.Physiol Rev. 2019 Jan 1;99(1):513-554. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00001.2018. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30427276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The draft genome of the microscopic Nemertoderma westbladi sheds light on the evolution of Acoelomorpha genomes.Front Genet. 2023 Sep 26;14:1244493. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1244493. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37829276 Free PMC article.
-
Lung epithelium development and airway regeneration.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 10;10:1022457. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1022457. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36299482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osr1 Is a Critical Regulator of Macrophage Polarization in NASH Progression.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;15(5):1249-1250. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.01.009. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36801205 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bai CB, Auerbach W, Lee JS, Stephen D, Joyner AL. Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development. 2002;129:4753–4761. - PubMed
-
- Bai CB, Joyner AL. Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2. Development. 2001;128:5161–5172. - PubMed
-
- Grindley JC, Bellusci S, Perkins D, Hogan BL. Evidence for the involvement of the Gli gene family in embryonic mouse lung development. Developmental biology. 1997;188:337–348. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

