Cyst-Like Osteolytic Formations in Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhBMP-2) Augmented Sheep Spinal Fusion
- PMID: 28502475
- PMCID: PMC5500826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.03.010
Cyst-Like Osteolytic Formations in Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhBMP-2) Augmented Sheep Spinal Fusion
Abstract
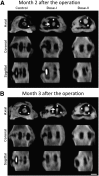
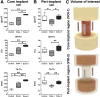
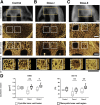
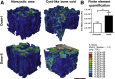
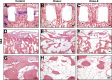
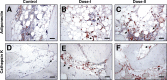
Multiple case reports using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) have reported complications. However, the local adverse effects of rhBMP-2 application are not well documented. In this report we show that, in addition to promoting lumbar spinal fusion through potent osteogenic effects, rhBMP-2 augmentation promotes local cyst-like osteolytic formations in sheep trabecular bones that have undergone anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Three months after operation, conventional computed tomography showed that the trabecular bones of the rhBMP-2 application groups could fuse, whereas no fusion was observed in the control group. Micro-computed tomography analysis revealed that the core implant area's bone volume fraction and bone mineral density increased proportionately with rhBMP-2 dose. Multiple cyst-like bone voids were observed in peri-implant areas when using rhBMP-2 applications, and these sites showed significant bone mineral density decreases in relation to the unaffected regions. Biomechanically, these areas decreased in strength by 32% in comparison with noncystic areas. Histologically, rhBMP-2-affected void sites had an increased amount of fatty marrow, thinner trabecular bones, and significantly more adiponectin- and cathepsin K-positive cells. Despite promoting successful fusion, rhBMP-2 use in clinical applications may result in local adverse structural alterations and compromised biomechanical changes to the bone.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Burkus J.K., Sandhu H.S., Gornet M.F., Longley M.C. Use of rhBMP-2 in combination with structural cortical allografts: clinical and radiographic outcomes in anterior lumbar spinal surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:1205–1212. - PubMed
-
- Mesfin A., Buchowski J.M., Zebala L.P., Bakhsh W.R., Aronson A.B., Fogelson J.L., Hershman S., Kim H.J., Ahmad A., Bridwell K.H. High-dose rhBMP-2 for adults: major and minor complications: a study of 502 spine cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95:1546–1553. - PubMed
-
- Knox J.B., Dai J.M., III, Orchowski J. Osteolysis in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bone morphogenetic protein-2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2011;36:672–676. - PubMed
-
- Garrett M.P., Kakarla U.K., Porter R.W., Sonntag V.K. Formation of painful seroma and edema after the use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in posterolateral lumbar spine fusions. Neurosurgery. 2010;66:1044–1049. discussion 1049. - PubMed
-
- McClellan J.W., Mulconrey D.S., Forbes R.J., Fullmer N. Vertebral bone resorption after transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP-2) J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19:483–486. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

