Review of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitory Assay: Rapid Method in Drug Discovery of Herbal Plants
- PMID: 28503045
- PMCID: PMC5414448
- DOI: 10.4103/phrev.phrev_45_16
Review of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitory Assay: Rapid Method in Drug Discovery of Herbal Plants
Abstract
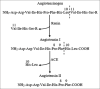
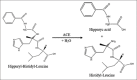
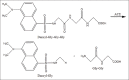
The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a signaling pathway which responsible in the blood pressure regulation. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is one of the key elements responsible for the hypertensive mechanism. It converts angiotensin-I to angiotensin-II. The discovery history of the ACE inhibitory activity assay method has been through a long stage for decades and development continues until today. The ACE inhibitory activity has become an effective screening method in the search for new antihypertensive agents from herbal plants. Some of in vitro assay methods were used to examine the activity of ACE inhibitors based on the substrate usage, such as; Cushman and Cheung Method using a substrate hippuryl-histidyl-leucine (HHL), Holmquist method using a substrate furanacryloyl-tripeptide, Elbl and Wagner method using a substrate benzoil-[l-14C] glicyl-L-histidine-L-leucine, Carmel and Yaron method using a substrate o-aminobenzoylglycyl-p-nitrophenylalanilproline, and Lam method using 3-hydroxybutyrylglycyl-glycyl-glycine as substrate. Several different methods to measure the results of enzymatic reactions or separating substrate with products, including spectrophotometric, fluorometric, high-performance liquid chromatography, electrophoresis, and radiochemistry. Application of the test method for screening the ACE inhibitors activity and investigation of active compounds from natural products can be done easily with this method, it is very helpful in research because the results obtained are simple, accurate, and rapid.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity; Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; angiotensin-converting enzyme; herbal plants; in vitro assay method.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- López-Fandiño R, Otte J, Camp JV. Physiological, chemical and technological aspects of milk-protein-derived peptides with antihypertensive and ACE-inhibitory activity. Int Dairy J. 2006;16:1277–93.
-
- Fujita M, Ohnishi K, Takaoka S, Ogasawara K, Fukuyama R, Nakamuta H. Antihypertensive effects of continuous oral administration of nattokinase and its fragments in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34:1696–701. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
