Trends with neoadjuvant radiotherapy and clinical staging for those with rectal malignancies
- PMID: 28503257
- PMCID: PMC5406733
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v9.i4.97
Trends with neoadjuvant radiotherapy and clinical staging for those with rectal malignancies
Abstract
Aim: To see how patterns of care changed over time, and how institution type effected these decisions.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed using the National Cancer Database, looking at all patients that were diagnosed with rectal cancer from 1998 to 2011. We tested differences in rates of treatment and stage migration using χ2 tests and logistic regression models.
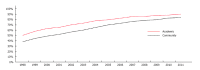
Results: A review of ninety thousand five hundred and ninety four subjects underwent multimodality therapy for cancer of the rectum. Staging and response to treatment varied greatly between centers. Forty-six percent of the time staging was missing in academic practices, vs fifty-four percent of the time in community centers (P < 0.001). As a result, twenty-percent were down-staged and eight percent up-staged in academia, whereas only fifteen percent were down-staged and 8% up-staged in community practices (P < 0.001). Forty-two percent of individuals underwent radiation before surgery in 1998. Within two years this increased to fifty-three percent. This increased to eighty-six percent by 2011 (P < 0.001). Institution specific treatment varied greatly. Fifty-one percent received therapy before surgery in academic centers in 1998. Thirty-nine percent followed this pattern in the same year in the community (P < 0.001). By 2011, ninety-one percent received radiation before their procedure in academic centers, vs eighty-four percent in the community (P < 0.001). Rates of adoption were better in academia, although an increase was seen in both center types.
Conclusion: From the study dates of 1998 to 2011, preoperative treatment with radiation has been on the rise. There is certainly an increased rate of use of radiation in academia, however, this trend is also seen in the community. Practice patterns have evolved over time, although rates of assigning clinical stage are grossly underreported prior to initiation of preoperative therapy.
Keywords: Academic; Community; Neoadjuvant therapy; Rectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no financial relationships to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiotherapy, concomitant protracted-venous-infusion 5-fluorouracil, and surgery for ultrasound-staged T3 or T4 rectal cancer.Dis Colon Rectum. 2001 Jan;44(1):52-8. doi: 10.1007/BF02234821. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001. PMID: 11805563 Clinical Trial.
-
Is the Pathologic Response of T3 Rectal Cancer to High-Dose-Rate Endorectal Brachytherapy Comparable to External Beam Radiotherapy?Dis Colon Rectum. 2019 Mar;62(3):294-301. doi: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001220. Dis Colon Rectum. 2019. PMID: 30741768
-
The national practice for patients receiving radiation therapy for carcinoma of the esophagus: results of the 1996-1999 Patterns of Care Study.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 Jul 15;56(4):981-7. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00256-6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 12829133
-
Neoadjuvant therapy for adenocarcinoma of the rectum: tumor response and acute toxicity.Dis Colon Rectum. 2001 Apr;44(4):513-22. doi: 10.1007/BF02234323. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001. PMID: 11330578
-
Neoadjuvant radiotherapy for rectal cancer management.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 7;25(33):4850-4869. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i33.4850. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31543678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Patterns of Rectal Cancer Radiotherapy Adopting Evidence-Based Medicine: An Analysis of the National Database from 2005 to 2016.Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jul;50(3):975-983. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.459. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29081217 Free PMC article.
-
IntAct: intra-operative fluorescence angiography to prevent anastomotic leak in rectal cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial.Colorectal Dis. 2018 Aug;20(8):O226-O234. doi: 10.1111/codi.14257. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Colorectal Dis. 2018. PMID: 29751360 Free PMC article.
-
A 25 year experience of perineal hernia repair.Hernia. 2020 Apr;24(2):273-278. doi: 10.1007/s10029-019-01958-0. Epub 2019 May 2. Hernia. 2020. PMID: 31049717
References
-
- Cass AW, Million RR, Pfaff WW. Patterns of recurrence following surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1976;37:2861–2865. - PubMed
-
- Mendenhall WM, Million RR, Pfaff WW. Patterns of recurrence in adenocarcinoma of the rectum and rectosigmoid treated with surgery alone: implications in treatment planning with adjuvant radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1983;9:977–985. - PubMed
-
- Hoffe SE, Shridhar R, Biagioli MC. Radiation therapy for rectal cancer: current status and future directions. Cancer Control. 2010;17:25–34. - PubMed
-
- Minsky BD, Mies C, Recht A, Rich TA, Chaffey JT. Resectable adenocarcinoma of the rectosigmoid and rectum. I. Patterns of failure and survival. Cancer. 1988;61:1408–1416. - PubMed
-
- Heald RJ, Ryall RD. Recurrence and survival after total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Lancet. 1986;1:1479–1482. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials