An assessment of patient waiting and consultation time in a primary healthcare clinic
- PMID: 28503269
- PMCID: PMC5420318
An assessment of patient waiting and consultation time in a primary healthcare clinic
Abstract
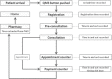
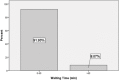
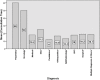
Waiting is a common phenomenon in the doctor's waiting room. The purpose of this audit is to assess patient waiting time and doctor consultation time in a primary healthcare clinic and to formulate strategies for improvement. This audit was conducted at a primary care clinic for 4 weeks using the universal sampling method. All patients who attended the clinic during this period was included in the study except for those who required more time to be seen such as those who were critically ill, aggressive or those who came for repeat medication or procedures only without needing to see the doctor. The time of arrival was captured using the queue management system (QMS) and then the patient was given a timing chit which had to be manually filled by the staff at every station. The waiting time for registration, pre-consultation, consultation, appointment, payment and pharmacy were recorded as well as consultation time. The data were entered into the statistical software SPSS version 17 for analysis. version 17. Results showed that more than half of the patients were registered within 15 minutes (53%) and the average total waiting time from registration to seeing a doctor was 41 minutes. Ninety-nine percentage of patients waited less than 30 minutes to get their medication. The average consultation time was 18.21 minutes. The problems identified in this audit were addressed and strategies formulated to improve the waiting and consultation time were carried out including increasing the number of staff at the registration counter, enforcing the staggered appointment system for follow-up patients and improving the queuing system for walk-in patients.
Keywords: Clinical audit; consultation time; general practice; patient waiting time; primary care.
Figures

References
-
- Kintz J. This Book Is Not for Sale. Ebook; 2011.
-
- Hassali MA, Alrasheedy AA, Ab Razak BA. et al. Assessment of general public satisfaction with public healthcare services in Kedah, Malaysia. [Accessed Jan 11;2017 ];AMJ. 2014 7(1):35–44. http//dx.doi.org/10.4066/AMJ.2014.1936 Available at: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manaf NHA, Phang SN. Patient satisfaction as an indicator of service quality in Malaysian public hospitals. [Accessed Jan 11;2017 ];Asian J Qual. 2009 10(1):77–87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/15982680980000628 Available at: - DOI
-
- McKinnon K, Crofts PD, Rhiannon E. et al. The outpatient experience: results of a patient feedback survey. Int J Health Care Qual Assur Inc Leadersh Health Serv. 2006;11(5):156–60. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/09526869610230858 Available at: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kujala J, Lillrang P, Kronström V. Time-based management of patient processes. [Accessed Jan 11;2017 ];J Health Organ Manag. 2006 20(6):512–24. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/14777260610702262 Available at: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
