Acute Postviral Encephalopathy: Pathologic and Radiologic Correlation in an Atypical Case
- PMID: 28503611
- PMCID: PMC5417279
- DOI: 10.1177/2329048X16658845
Acute Postviral Encephalopathy: Pathologic and Radiologic Correlation in an Atypical Case
Abstract
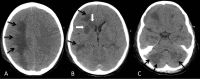
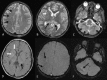
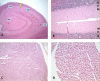
The authors report a case of fatal acute encephalopathy following influenza infection, with slightly atypical pathological and imaging findings. A healthy 8-year-old boy with probable recent influenza A/B infection admitted for refractory seizures was placed on phenobarbital coma and later developed hemodynamic instability. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed bilateral cerebral and cerebellar white matter lesions and microhemorrhages. Following his demise, the autopsy revealed a large area of necrosis in the right centrum semiovale with similar lesions in the temporal and cerebellar regions. Microscopically, there was extensive coagulative necrosis, compatible with necrotizing white matter encephalopathy, and neuronal loss suggesting superimposed hypoxic-ischemia. The acute progressive neurologic deterioration was partly reminiscent on acute necrotizing encephalopathy, a condition recently associated with influenza A. In acute necrotizing encephalopathy, typical brain findings are characterized by bilateral thalamic necrosis/petechiae with variable white matter edema. The somewhat atypical findings in our case can relate to superadded cardiovascular collapse and hypoxic-ischemic effects.
Keywords: acute necrotizing encephalopathy; influenza-associated encephalopathy; postviral.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Tabarki B, Thabet F, Al Shafi S, Al Adwani N, Chehab M, Al Shahwan S. Acute necrotizing encephalopathy associated with enterovirus infection. Brain Dev. 2013;35(5):454–457. - PubMed
-
- Newland JG, Laurich VM, Rosenquist AW, et al. Neurologic complications in children hospitalized with influenza: characteristics, incidence, and risk factors. J Pediatr. 2007;150(3):306–310. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

