Risk of death from cardiovascular disease following breast cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 28503723
- PMCID: PMC5495872
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-017-4282-9
Risk of death from cardiovascular disease following breast cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer incidence and survival is high, which results in high prevalence of breast cancer survivors. The risk of (death from) cardiovascular disease (CVD) is higher in patients exposed to cardiotoxic treatments, in particular if they have pre-existing CVD risk factors. This study systematically summarized the risk of death from CVD following breast cancer.
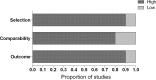
Methods: Databases of Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Library were systematically searched using the following terms and synonyms: breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cause of death. Articles reporting on both risk and risk factors of CVD mortality following breast cancer were eligible for inclusion. The methodological quality of each article was assessed using the Newcastle Ottawa quality assessment scale for cohort studies.
Results: Fourteen articles were included assessing the risk of CVD mortality among 1,217,910 women with breast cancer. The methodological quality was high for the majority of the studies. Studies were heterogeneous in design, study population, length of follow-up, CVD outcomes, and risk factors. 1.6-10.4% of all women with breast cancer died of CVD. Women with breast cancer had a higher risk of CVD mortality than women from the general population. The risk of CVD mortality was higher among women with breast cancer with older age at diagnosis, left-sided tumor, diagnosis in an earlier calendar period, and black ethnic origin.
Conclusions: CVD is an important cause of death following breast cancer. Identification of patients at high risk of CVD is important to optimize CVD prevention and tailor breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Absolute risk; Breast cancer; Cardiovascular disease; Risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study format, informed consent is not required. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Integraal Kankercentrum Nederland Cijfers over kanker. http://cijfersoverkanker.nl/. Accessed 10 Aug 2016
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration, Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R, Dandona L, Fleming T, Forouzanfar MH, Hancock J, Hay RJ, Hunter-Merrill R, Huynh C, Hosgood HD, Johnson CO, Jonas JB, Khubchandani J, Kumar GA, Kutz M, Lan Q, Larson HJ, Liang X, Lim SS, Lopez AD, MacIntyre MF, Marczak L, Marquez N, Mokdad AH, Pinho C, Pourmalek F, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Sandar L, Sartorius B, Schwartz SM, Shackelford KA, Shibuya K, Stanaway J, Steiner C, Sun J, Takahashi K, Vollset SE, Vos T, Wagner JA, Wang H, Westerman R, Zeeb H, Zoeckler L, Abd-Allah F, Ahmed MB, Alabed S, Alam NK, Aldhahri SF, Alem G, Alemayohu MA, Ali R, Al-Raddadi R, Amare A, Amoako Y, Artaman A, Asayesh H, Atnafu N, Awasthi A, Saleem HB, Barac A, Bedi N, Bensenor I, Berhane A, Bernabe E, Betsu B, Binagwaho A, Boneya D, Campos-Nonato I, Castaneda-Orjuela C, Catala-Lopez F, Chiang P, Chibueze C, Chitheer A, Choi JY, Cowie B, Damtew S, das Neves J, Dey S, Dharmaratne S, Dhillon P, Ding E, Driscoll T, Ekwueme D, Endries AY, Farvid M, Farzadfar F, Fernandes J, Fischer F, G/Hiwot TT, Gebru A, Gopalani S, Hailu A, Horino M, Horita N, Husseini A, Huybrechts I, Inoue M, Islami F, Jakovljevic M, James S, Javanbakht M, Jee SH, Kasaeian A, Kedir MS, Khader YS, Khang YH, Kim D, Leigh J, Linn S, Lunevicius R, El Razek HM, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Marcenes W, Markos D, Melaku YA, Meles KG, Mendoza W, Mengiste DT, Meretoja TJ, Miller TR, Mohammad KA, Mohammadi A, Mohammed S, Moradi-Lakeh M, Nagel G, Nand D, Le Nguyen Q, Nolte S, Ogbo FA, Oladimeji KE, Oren E, Pa M, Park EK, Pereira DM, Plass D, Qorbani M, Radfar A, Rafay A, Rahman M, Rana SM, Soreide K, Satpathy M, Sawhney M, Sepanlou SG, Shaikh MA, She J, Shiue I, Shore HR, Shrime MG, So S, Soneji S, Stathopoulou V, Stroumpoulis K, Sufiyan MB, Sykes BL, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tessema GA, Thakur JS, Tran BX, Ukwaja KN, Uzochukwu BS, Vlassov VV, Weiderpass E, Wubshet Terefe M, Yebyo HG, Yimam HH, Yonemoto N, Younis MZ, Yu C, Zaidi Z, Zaki ME, Zenebe ZM, Murray CJ, Naghavi M (2016) Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, Mandelblatt JS, Yakovlev AY, Habbema JD, Feuer EJ, Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) Collaborators Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1784–1792. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050518. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

