Actomyosin meshwork mechanosensing enables tissue shape to orient cell force
- PMID: 28504247
- PMCID: PMC5440693
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15014
Actomyosin meshwork mechanosensing enables tissue shape to orient cell force
Abstract
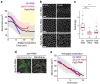
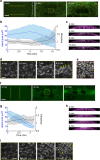
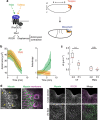
Sculpting organism shape requires that cells produce forces with proper directionality. Thus, it is critical to understand how cells orient the cytoskeleton to produce forces that deform tissues. During Drosophila gastrulation, actomyosin contraction in ventral cells generates a long, narrow epithelial furrow, termed the ventral furrow, in which actomyosin fibres and tension are directed along the length of the furrow. Using a combination of genetic and mechanical perturbations that alter tissue shape, we demonstrate that geometrical and mechanical constraints act as cues to orient the cytoskeleton and tension during ventral furrow formation. We developed an in silico model of two-dimensional actomyosin meshwork contraction, demonstrating that actomyosin meshworks exhibit an inherent force orienting mechanism in response to mechanical constraints. Together, our in vivo and in silico data provide a framework for understanding how cells orient force generation, establishing a role for geometrical and mechanical patterning of force production in tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
-
- Vignaud T. et al. Reprogramming cell shape with laser nano-patterning. J. Cell Sci. 125, 2134–2140 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Théry M., Pépin A., Dressaire E., Chen Y. & Bornens M. Cell distribution of stress fibres in response to the geometry of the adhesive environment. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 63, 341–355 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

