Legionella effector Lpg1137 shuts down ER-mitochondria communication through cleavage of syntaxin 17
- PMID: 28504273
- PMCID: PMC5440676
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15406
Legionella effector Lpg1137 shuts down ER-mitochondria communication through cleavage of syntaxin 17
Abstract
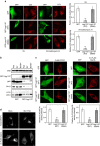
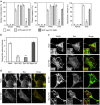
During infection of macrophages, the pathogenic bacterium Legionella pneumophila secretes effector proteins that induce the conversion of the plasma membrane-derived vacuole into an endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-like replicative vacuole. These ER-like vacuoles are ultimately fused with the ER, where the pathogen replicates. Here we show that the L. pneumophila effector Lpg1137 is a serine protease that targets the mitochondria and their associated membranes. Lpg1137 binds to and cleaves syntaxin 17, a soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) protein that is known to participate in the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics through interaction with the mitochondrial fission factor Drp1 in fed cells and in autophagy through interaction with Atg14L and other SNAREs in starved cells. Cleavage of syntaxin 17 inhibits not only autophagy but also staurosporine-induced apoptosis occurring in a Bax, Drp1-dependent manner. Thus, L. pneumophila can shut down ER-mitochondria communication through cleavage of syntaxin 17.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

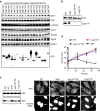
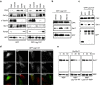
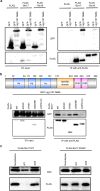
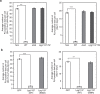

References
-
- Hubber A. & Roy C. R. Modulation of host cell function by Legionella pneumophila type IV effectors. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 26, 261–283 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Asrat S., de Jesús D. A., Hempstead A. D., Ramabhadran V. & Isberg R. R. Bacterial pathogen manipulation of host membrane trafficking. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 30, 79–109 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

