A Subset of Malignant Mesotheliomas in Young Adults Are Associated With Recurrent EWSR1/FUS-ATF1 Fusions
- PMID: 28505004
- PMCID: PMC5468482
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000864
A Subset of Malignant Mesotheliomas in Young Adults Are Associated With Recurrent EWSR1/FUS-ATF1 Fusions
Abstract
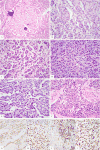
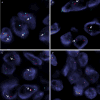
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is a rare, aggressive tumor often associated with asbestos exposure and characterized by complex genetic abnormalities, including deletions of chromosome 22. A gene fusion involving EWSR1 and YY1 gene on 14q32 has been reported in 2 patients over the age of 60 with peritoneal MM. However, the incidence of EWSR1 rearrangements in MM and the spectrum of its fusion partners remain unknown. We recently encountered 2 MM cases with EWSR1-ATF1 fusions and sought to investigate the prevalence and clinicopathologic features associated with this abnormality. As both index cases occurred as intra-abdominal tumors in young adults, we searched our files for pleural and peritoneal MM occurring in adults younger than age of 40. All cases were tested by fluorescence in situ hybridization using custom bacterial artificial chromosomes probes for EWSR1, FUS, and ATF1 genes. When available, immunohistochemistry for BAP1 was performed. A total of 25 MM from patients aged 40 or less were screened, either from peritoneum (n=13) or pleura (n=12), with a median age of 31 (range: 7 to 40 y). Two additional ATF1-rearranged tumors were identified at pleural and peritoneal sites with EWSR1 and FUS as fusion partners, respectively, for a total of 4 cases (16%, 4/25). The fusion-positive cases displayed classic epithelioid morphology, immunoreactivity for cytokeratins and WT1, and negativity for S100. BAP1 expression was retained in the 3 fusion-positive cases with available material, and in 80% (12/15) of the fusion-negative cases. Our results expand the spectrum of tumor types harboring EWSR1/FUS-ATF1 gene fusions to include a subgroup of conventional epithelioid MM. Other features of this unique MM subset include young age at presentation, lack of asbestos exposure and retained BAP1 expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EWSR1::YY1 fusion positive peritoneal epithelioid mesothelioma harbors mesothelioma epigenetic signature: Report of 3 cases in support of an emerging entity.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2022 Oct;61(10):592-602. doi: 10.1002/gcc.23074. Epub 2022 Jun 24. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35665561 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokeratin-positive Malignant Tumor in the Abdomen With EWSR1/FUS-CREB Fusion: A Clinicopathologic Study of 8 Cases.Am J Surg Pathol. 2022 Jan 1;46(1):134-146. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001742. Am J Surg Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34049318
-
Update on gene fusions and the emerging clinicopathological landscape of peritoneal and pleural mesotheliomas and other neoplasms.ESMO Open. 2024 Aug;9(8):103644. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.103644. Epub 2024 Jul 25. ESMO Open. 2024. PMID: 39059063 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing the distribution of alterations in mesothelioma and their correlation to morphology.Am J Clin Pathol. 2023 Sep 1;160(3):238-246. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqad041. Am J Clin Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37141416 Review.
-
Malignant Mesothelioma and Its Non-Asbestos Causes.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018 Jun;142(6):753-760. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0365-RA. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29480760 Review.
Cited by
-
The oncogenic properties of the EWSR1::CREM fusion gene are associated with polyamine metabolism.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 25;13(1):4884. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31576-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36966162 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights and recent discoveries on the genetics and pathogenesis of malignant mesothelioma.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Mar;10(3):1314-1317. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.03.33. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29708148 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Malignant Mesothelioma With EWSR1-ATF1 Fusion in Two Adolescent Male Patients.Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2021 Nov-Dec;24(6):570-574. doi: 10.1177/10935266211021222. Epub 2021 Jun 12. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2021. PMID: 34121509 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive genomic profiling of EWSR1/FUS::CREB translocation-associated tumors uncovers prognostically significant recurrent genetic alterations and methylation-transcriptional correlates.Mod Pathol. 2022 Aug;35(8):1055-1065. doi: 10.1038/s41379-022-01023-9. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Mod Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35347249 Free PMC article.
-
Soft Tissue Special Issue: Adamantinoma-Like Ewing Sarcoma of the Head and Neck: A Practical Review of a Challenging Emerging Entity.Head Neck Pathol. 2020 Mar;14(1):59-69. doi: 10.1007/s12105-019-01098-y. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Head Neck Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31950471 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moolgavkar SH, Meza R, Turim J. Pleural and peritoneal mesotheliomas in SEER: age effects and temporal trends, 1973–2005. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20:935–944. - PubMed
-
- Reid A, de Klerk NH, Magnani C, et al. Mesothelioma risk after 40 years since first exposure to asbestos: a pooled analysis. Thorax. 2014;69:843–850. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

