Attenuation of Drought Stress in Brassica Seedlings with Exogenous Application of Ca2+ and H₂O₂
- PMID: 28505096
- PMCID: PMC5489792
- DOI: 10.3390/plants6020020
Attenuation of Drought Stress in Brassica Seedlings with Exogenous Application of Ca2+ and H₂O₂
Abstract
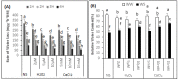
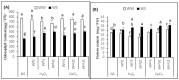
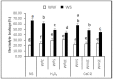
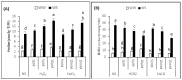
Drought is one of the most common abiotic stresses, affecting the growth and productivity of crop plants globally, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. Different strategies are used to mitigate the impact of drought among crop plants. Exogenous application of different substances are known to decrease the effects of various abiotic stresses, including drought stress. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of Ca2+ and H₂O₂ in developing drought stress tolerance in Brassica napus "Bulbul-98" seedlings. Brassica napus "Bulbul-98" seedlings were exposed to 5, 10 and 15 mM Ca2+ and 2, 5 and 10 μM H₂O₂ concentrations twice at an interval of two days for up to 20 days after germination. Drought stress decreased relative water content (RWC), chlorophyll content and increased proline, H₂O₂, soluble protein and electrolyte leakage in Brassica seedlings. Exogenous Ca2+ (5, 10,15 mM) and H₂O₂ (2, 5, 10 μM) supplementations, during drought stress induction, showed a significant increase in RWC by 5.4%, 18.06%, 26.2% and 6.87%, 13.9%, 18.3% respectively. Similarly, with the exogenous application of Ca2+ (5, 10, 15 mM) and H₂O₂ (2, 5, 10 μM), chlorophyll content was increased by 15.03%, 22.2%, and 28.4%, and 9.6%, 23.3%, and 27.5% respectively. It was confirmed that the seedlings under drought stress that were supplemented with Ca2+ and H₂O₂ recovered from water content reduction and chlorosis, and were able to grow normally.
Keywords: SDS-PAGE; drought stress; electrolyte leakage; proline; relative water content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bajji M., Kinet J.M., Lutts S. The use of the electrolyte leakage method for assessing cell membrane stability as a water stress tolerance test in durum wheat. J. Plant Growth Reg. 2002;36:61–70. doi: 10.1023/A:1014732714549. - DOI
-
- Hsu S.Y., Hsu Y.T., Kao C.H. The effect of polyethylene glycol on proline accumulation in rice leaves. Biol. Plant. 2003;46:73–78. doi: 10.1023/A:1022362117395. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

