Investigation of the effect of cochlear implant electrode length on speech comprehension in quiet and noise compared with the results with users of electro-acoustic-stimulation, a retrospective analysis
- PMID: 28505158
- PMCID: PMC5432071
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174900
Investigation of the effect of cochlear implant electrode length on speech comprehension in quiet and noise compared with the results with users of electro-acoustic-stimulation, a retrospective analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This investigation evaluated the effect of cochlear implant (CI) electrode length on speech comprehension in quiet and noise and compare the results with those of EAS users.
Methodes: 91 adults with some degree of residual hearing were implanted with a FLEX20, FLEX24, or FLEX28 electrode. Some subjects were postoperative electric-acoustic-stimulation (EAS) users; the other subjects were in the groups of electric stimulation-only (ES-only). Speech perception was tested in quiet and noise at 3 and 6 months of ES or EAS use. Speech comprehension results were analyzed and correlated to electrode length.
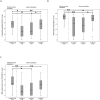
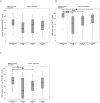
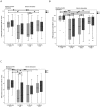
Results: While the FLEX20 ES and FLEX24 ES groups were still in their learning phase between the 3 to 6 months interval, the FLEX28 ES group was already reaching a performance plateau at the three months appointment yielding remarkably high test scores. EAS subjects using FLEX20 or FLEX24 electrodes outscored ES-only subjects with the same short electrodes on all 3 tests at each interval, reaching significance with FLEX20 ES and FLEX24 ES subjects on all 3 tests at the 3-months interval and on 2 tests at the 6- months interval. Amongst ES-only subjects at the 3- months interval, FLEX28 ES subjects significantly outscored FLEX20 ES subjects on all 3 tests and the FLEX24 ES subjects on 2 tests. At the-6 months interval, FLEX28 ES subjects still exceeded the other ES-only subjects although the difference did not reach significance.
Conclusions: Among ES-only users, the FLEX28 ES users had the best speech comprehension scores, at the 3- months appointment and tendentially at the 6 months appointment. EAS users showed significantly better speech comprehension results compared to ES-only users with the same short electrodes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- von Ilberg CA, Baumann U, Kiefer J, Tillein J, Adunka OF. Electric-acoustic stimulation of the auditory system: a review of the first decade. Audiol Neurootol. 2011;16 Suppl 2:1–30. Epub 2011 May 24. - PubMed
-
- Büchner A, Schüssler M, Battmer RD, Stöver T, Lesinski-Schiedat A, Lenarz T. Impact of low-frequency hearing. Audiol Neurotol 2009;14 Suppl 1:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Lenarz T, Stöver T, Buechner A, Paasche G, Briggs R, Risi F, et al. Temporal bone results and hearing preservation with a new straight electrode. Audiol Neurotol 2006;11 Suppl 1:34–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

