Editor's Highlight: Farnesoid X Receptor Protects Against Low-Dose Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury Through the Taurocholate-JNK Pathway
- PMID: 28505368
- PMCID: PMC5837376
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx094
Editor's Highlight: Farnesoid X Receptor Protects Against Low-Dose Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Injury Through the Taurocholate-JNK Pathway
Abstract
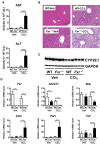
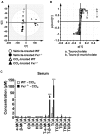
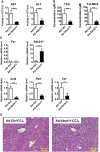
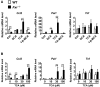
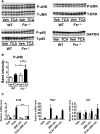
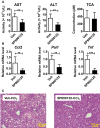
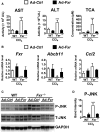
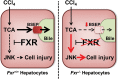
Hepatotoxicity is of major concern for humans exposed to industrial chemicals and drugs. Disruption of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a master regulator of bile acid (BA) metabolism, enhanced the sensitivity to liver injury in mice after toxicant exposure, but the precise mechanism remains unclear. In this study, the interconnection between BA metabolism, FXR, and chemically induced hepatotoxicity was investigated using metabolomics, Fxr-null mice (Fxr-/-) and hepatocytes, and recombinant adenoviruses. A single low-dose intraperitoneal injection of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), an inducer of acute hepatitis in mice, resulted in more severe hepatocyte damage and higher induction of pro-inflammatory mediators, such as chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (Ccl2), in Fxr-/-. Serum metabolomics analysis revealed marked increases in circulating taurocholate (TCA) and tauro-β-muricholate (T-β-MCA) in these mice, and forced expression of bile salt export protein (BSEP) by recombinant adenovirus in Fxr-/- ameliorated CCl4-induced liver damage. Treatment of Fxr-null hepatocytes with TCA, but not T-β-MCA, significantly increased c-Jun-N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation and Ccl2 mRNA levels, and up-regulation of Ccl2 mRNA was attenuated by co-treatment with a JNK inhibitor SP600125, indicating that TCA directly amplifies hepatocyte inflammatory signaling mainly mediated by JNK under FXR-deficiency. Additionally, pretreatment with SP600125 or restoration of FXR expression in liver by use of recombinant adenovirus, attenuated CCl4-induced liver injury. Collectively, these results suggest that the TCA-JNK axis is likely associated with increased susceptibility to CCl4-induced acute liver injury in Fxr-/-, and provide clues to the mechanism by which FXR and its downstream gene targets, such as BSEP, protects against chemically induced hepatotoxicity.
Keywords: CCl4; bile acids; c-Jun-N-terminal kinase; farnesoid X receptor; taurocholate.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society of Toxicology 2017. This work is written by US Government employees and is in the public domain in the United States.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obeticholic acid protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury and inflammation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 1;314:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.11.006. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27865854
-
Hepatoprotective properties of sesamin against CCl4 induced oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in mice via JNK pathway.Food Chem Toxicol. 2014 Feb;64:41-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.017. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Food Chem Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24287204
-
Geniposidic acid protected against ANIT-induced hepatotoxity and acute intrahepatic cholestasis, due to Fxr-mediated regulation of Bsep and Mrp2.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.033. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26723467
-
Bile salt excretory pump: biology and pathobiology.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006 Jul;43 Suppl 1:S10-6. doi: 10.1097/01.mpg.0000226385.71859.5f. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2006. PMID: 16819395 Review.
-
The Farnesoid X Receptor as a Master Regulator of Hepatotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 12;23(22):13967. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213967. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Celastrol ameliorates acute liver injury through modulation of PPARα.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;178:114058. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114058. Epub 2020 May 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32470546 Free PMC article.
-
The role of farnesoid X receptor in metabolic diseases, and gastrointestinal and liver cancer.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May;18(5):335-347. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-00404-2. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33568795 Review.
-
Farnesoid X receptor: a potential therapeutic target in multiple organs.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Dec;35(12):1403-1414. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-301. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 33393073 Review.
-
Taurocholic Acid and Glycocholic Acid Inhibit Inflammation and Activate Farnesoid X Receptor Expression in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish and Macrophages.Molecules. 2023 Feb 21;28(5):2005. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052005. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36903252 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Farnesoid X Receptor and Bile Acids in Hepatic Tumor Development.Hepatol Commun. 2018 Oct 1;2(12):1567-1582. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1263. eCollection 2018 Dec. Hepatol Commun. 2018. PMID: 30556042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avasarala S., Yang L., Sun Y., Leung A. W., Chan W. Y., Cheung W. T., Lee S. S. (2006). A temporal study on the histopathological, biochemical and molecular responses of CCl(4)-induced hepatotoxicity in Cyp2e1-null mice. Toxicology 228, 310–322. - PubMed
-
- Baeck C., Wehr A., Karlmark K. R., Heymann F., Vucur M., Gassler N., Huss S., Klussmann S., Eulberg D., Luedde T., et al. (2012). Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury. Gut 61, 416–426. - PubMed
-
- Byrne J. A., Strautnieks S. S., Ihrke G., Pagani F., Knisely A. S., Linton K. J., Mieli-Vergani G., Thompson R. J. (2009). Missense mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCB11 impair bile salt export pump processing and function or disrupt pre-messenger RNA splicing. Hepatology 49, 553–567. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

