Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 28507210
- PMCID: PMC5399609
- DOI: 10.2337/db16-1477
Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
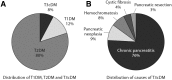
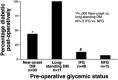
The relationships between diabetes and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) are complex. Longstanding type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is a risk factor for pancreatic cancer, but increasing epidemiological data point to PDAC as also a cause of diabetes due to unknown mechanisms. New-onset diabetes is of particular interest to the oncology community as the differentiation of new-onset diabetes caused by PDAC as distinct from T2DM may allow for earlier diagnosis of PDAC. To address these relationships and raise awareness of the relationships between PDAC and diabetes, a symposium entitled Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer was held at the American Diabetes Association's 76th Scientific Sessions in June 2016. This article summarizes the data presented at that symposium, describing the current understanding of the interrelationships between diabetes, diabetes management, and pancreatic cancer, and identifies areas where additional research is needed.
© 2017 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures


References
-
- Everhart J, Wright D. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis. JAMA 1995;273:1605–1609 - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:7–30 - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 2014;74:2913–2921 - PubMed

