When two wrongs make a right: synchronized neuronal bursting from combined electrical and inhibitory coupling
- PMID: 28507227
- PMCID: PMC5434073
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2016.0282
When two wrongs make a right: synchronized neuronal bursting from combined electrical and inhibitory coupling
Abstract
Synchronized cortical activities in the central nervous systems of mammals are crucial for sensory perception, coordination and locomotory function. The neuronal mechanisms that generate synchronous synaptic inputs in the neocortex are far from being fully understood. In this paper, we study the emergence of synchronization in networks of bursting neurons as a highly non-trivial, combined effect of electrical and inhibitory connections. We report a counterintuitive find that combined electrical and inhibitory coupling can synergistically induce robust synchronization in a range of parameters where electrical coupling alone promotes anti-phase spiking and inhibition induces anti-phase bursting. We reveal the underlying mechanism, which uses a balance between hidden properties of electrical and inhibitory coupling to act together to synchronize neuronal bursting. We show that this balance is controlled by the duty cycle of the self-coupled system which governs the synchronized bursting rhythm.This article is part of the themed issue 'Mathematical methods in medicine: neuroscience, cardiology and pathology'.
Keywords: bursting neurons; duty cycle; electrical coupling; inhibition; synchronization.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures




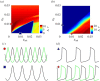



 (mV), calculated and averaged over four bursting periods. The black (blue) bounded region represents complete synchrony. Note the maximal area of stable synchrony in the network with both local electrical and inhibitory connections (d); this indicates that the combined synergistic effect is strongest in sparse configurations with connected graphs. (Online version in colour.)
(mV), calculated and averaged over four bursting periods. The black (blue) bounded region represents complete synchrony. Note the maximal area of stable synchrony in the network with both local electrical and inhibitory connections (d); this indicates that the combined synergistic effect is strongest in sparse configurations with connected graphs. (Online version in colour.)
Similar articles
-
Electrical coupling can prevent expression of adult-like properties in an embryonic neural circuit.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Jan;87(1):538-47. doi: 10.1152/jn.00372.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11784769
-
Analysis of synchronization between two modules of pulse neural networks with excitatory and inhibitory connections.Neural Comput. 2006 May;18(5):1111-31. doi: 10.1162/089976606776241039. Neural Comput. 2006. PMID: 16595059
-
Complex synchronous behavior in interneuronal networks with delayed inhibitory and fast electrical synapses.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2012 Jun;85(6 Pt 1):061905. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.85.061905. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2012. PMID: 23005125
-
[Synchronization and propagation of electrical potentials in neural networks of the brain cortex].Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2014 May-Jun;64(3):255-69. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova. 2014. PMID: 25723013 Review. Russian.
-
Synchronous neural activity and memory formation.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010 Apr;20(2):150-5. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.02.006. Epub 2010 Mar 18. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20303255 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Autapses on Synchronization in Neural Networks With Chemical Synapses.Front Syst Neurosci. 2020 Nov 30;14:604563. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2020.604563. eCollection 2020. Front Syst Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33328913 Free PMC article.
-
Early Development of the GABAergic System and the Associated Risks of Neonatal Anesthesia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12951. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312951. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneous pain dynamics characterized by stochasticity in neural recordings of awake humans with chronic pain.Pain. 2025 Mar 20;166(9):e261-e275. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003592. Pain. 2025. PMID: 40839664
-
Mathematical methods in medicine: neuroscience, cardiology and pathology.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017 Jun 28;375(2096):20170016. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2017.0016. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2017. PMID: 28507240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Churchland PS, Sejnowski TJ. 1994. The computational brain. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

