Notch1 regulates the JNK signaling pathway and increases apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 28507277
- PMCID: PMC5542231
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17434
Notch1 regulates the JNK signaling pathway and increases apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
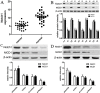
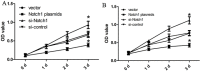
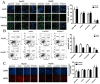
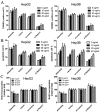
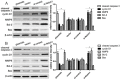
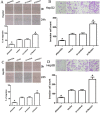
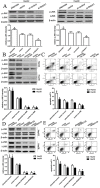
Notch1-induced pathways are involved in cell growth, apoptosis, motility, and invasion in many cancers. In the present study, the expression of Notch1 and NICD1 was detected in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues using in-vitro assays. And then, we explored cell biology and signaling pathways using Notch1 siRNA or plasmids. Here, the expression of Notch1 and NICD1 was significantly decreased in HCC tissues. In-vitro, Notch1 plasmids inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion, but enhanced apoptosis of HepG2 and Hep3B cells. Conversely, si-Notch1 enhanced cell proliferation, migration and invasion, but inhibited apoptosis of HepG2 and Hep3B cells. Mechanically, Notch1 decreased the expression of cyclin D1, MMP-9 and Bcl-2, but increased the expression of p-JNK, Bax and cleaved caspase 3 in HepG2 and Hep3B cells. Besides, si-JNK or JNK inhibitor SP600125 affected the activation of Notch1 signaling pathway, and prevents cell apoptosis. In conclusion, Notch1 regulates the JNK signaling pathway and increases apoptosis in HCC. Because patients with HCC have a poor prognosis, Notch1 pathway may provide a novel treatment strategy.
Keywords: HCC; JNK; Notch1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notch1 downregulation combined with interleukin-24 inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 7;21(33):9727-35. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9727. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26361419 Free PMC article.
-
Notch1 signaling inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.Cancer Res. 2003 Dec 1;63(23):8323-9. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14678992
-
Simvastatin induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in HepG2 and Huh7 hepatocellular carcinoma cells via upregulation of Notch1 expression.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Mar;11(3):2334-40. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2976. Epub 2014 Nov 19. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25412322
-
Suppressive effects of microRNA-16 on the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Dec;36(6):1713-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2379. Epub 2015 Oct 16. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26499886
-
Activation of the Notch1 Stem Cell Signaling Pathway during Routine Cell Line Subculture.Front Oncol. 2014 Aug 6;4:211. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00211. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25147757 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2018 Apr 12;9(9):1548-1559. doi: 10.7150/jca.24566. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29760792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR‑34c‑5p targets Notch1 and suppresses the metastasis and invasion of cervical cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Feb;23(2):120. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11759. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33300051 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of paradoxical genes: reevaluating the prognostic impact of overexpressed genes in cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 22;13:1525345. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1525345. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39911323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DAPT, a potent Notch inhibitor regresses actively growing abdominal aortic aneurysm via divergent pathways.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Jun 26;134(12):1555-1572. doi: 10.1042/CS20200456. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32490531 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Diagnostic Medical System Based on Notch1 Signaling Pathway to Inhibit the Growth of Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma.J Healthc Eng. 2022 May 19;2022:2311471. doi: 10.1155/2022/2311471. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9780157. doi: 10.1155/2023/9780157. PMID: 35646297 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Shinoda M, Kishida N, Itano O, Ei S, Ueno A, Kitago M, Abe Y, Hibi T, Yagi H, Masugi Y, Tanabe M, Aiura K, Sakamaoto M, et al. Long-term complete response of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated with multidisciplinary therapy including reduced dose of sorafenib: case report and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:144. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guo W, He X, Li Z, Li Y. Combination of transarterial chemoembolization (tace) and radiofrequency ablation (rfa) vs. surgical resection (sr) on survival outcome of early hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2015;62:710–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

