Effects of symbiotic and vitamin E supplementation on blood pressure, nitric oxide and inflammatory factors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 28507473
- PMCID: PMC5427479
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2016-846
Effects of symbiotic and vitamin E supplementation on blood pressure, nitric oxide and inflammatory factors in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
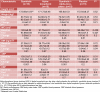
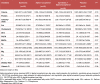
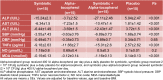
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been suggested to be well correlated with altered blood pressure. This study was conducted to determine the effects of symbiotic and vitamin E supplementation on blood pressure and inflammatory indices of patients with NAFLD. This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed among 60 NAFLD patients aged 25 to 64 years old. Participants were randomly divided into four groups to receive a 400 IU alpha-tocopherol and 2 × 108 CFU/g symbiotic supplement for 8 weeks. The anthropometric parameters, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), serum malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) were assessed at baseline and after 8 weeks of intervention. After 8 weeks of intervention, combined symbiotic and alpha-tocopherol, symbiotic and alpha-tocopherol alone administration, compared with the placebo, resulted in significant decreases in SBP (-17.07±2.1, -16.07±3.56, -1.73±2.25 and -1.55±3.01 mmHg, P=0.01), serum MDA (-1.19±0.5, -0.12±0.65, 0.14 ± 0.64 and 0.16±0.34 nmol/mL, P<0.001), serum TNFα (-15.62±13.93, -9.24±7.12, -11.44 ± 15.47 and 3.01±1.71 pg/ml, P<0.001) concentrations. A significant decrease in serum AST (-11.36±4.52, -7.43±8.58, -5.93±6.61 and 2.5±5.75 μmol/L, P <0.001), ALT (-12.79±3.65, -3.66±6.81, -6.54±7.66 and 4.16±3.43 μmol/L, P <0.001) and ALP (-26.8±11.1, -4.56±9.22, -14.48±12.22 and 5.19±2.64 μmol/L, P <0.001) was seen. Variations in DBP and serum NO concentration were not significant. Alpha-tocopherol and symbiotic supplementation among patients with NAFLD resulted in decreased SBP, serum MDA, TNFα levels and enzymes liver; however, they did not affect DBP and serum NO concentration.
Keywords: NAFLD; alpha-tocopherol; blood pressure; nitric oxide; symbiotic.
Figures

References
-
- Albillos A, de la Hera A, Gonzalez M, Moya JL, Calleja JL, Monserrat J, et al. Increased lipopolysaccharide binding protein in cirrhotic patients with marked immune and hemodynamic derangement. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2003;37:208–217. - PubMed
-
- Aller R, De Luis DA, Izaola O, Conde R, Gonzalez Sagrado M, Primo D, et al. Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2011;15:1090–1095. - PubMed
-
- Aqel B, DiBaise JK. Role of the gut microbiome in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr Clin Pract. 2015;30:780–786. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
