Diclofenac potassium for oral solution (CAMBIA®) in the acute management of a migraine attack: clinical evidence and practical experience
- PMID: 28507605
- PMCID: PMC5415228
- DOI: 10.1177/1756285616684494
Diclofenac potassium for oral solution (CAMBIA®) in the acute management of a migraine attack: clinical evidence and practical experience
Abstract
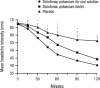
Migraine headache affects about 12% of Western populations and is the third most common disease worldwide (sixth in terms of disability). In 1993, triptans were introduced in the United States as a new treatment for managing migraine attacks, but their use is limited by lack of response and safety concerns in some patients. Treatment options for patients with migraine who fail or cannot tolerate triptans include switching to another medication or adding an adjunctive medication. Desirable characteristics reported by patients for acute treatment of migraine attacks include complete pain relief, fast onset of action, and no pain recurrence. Diclofenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medication that has been established as effective for acute treatment of migraine by the American Headache Society based on available evidence. Diclofenac potassium for oral solution is rapidly absorbed, achieving maximal plasma concentrations in 15 min, which coincides with a rapid onset of effect. In a comparison of diclofenac potassium for oral solution with diclofenac potassium tablets, the solution achieved a significant reduction in headache intensity beginning at 15 min compared with 60 min for the tablet. Across randomized clinical trials, approximately 25% of patients were pain free 2 h after administration of diclofenac oral solution and the effects were maintained over a 24-h period. Diclofenac potassium for oral solution is well tolerated; the most common adverse events are dizziness and gastrointestinal complaints, with incidences similar to placebo. No serious adverse events have been reported in clinical trials of diclofenac potassium for oral solution in the acute treatment of migraine. Diclofenac oral solution may offer rapid and sustained pain relief for patients who do not achieve pain resolution with other medications. In addition, patients who experience central sensitization with allodynia may benefit from the cyclooxygenase-blocking activity of diclofenac, which is needed in this advanced phase of migraine.
Keywords: diclofenac potassium for oral solution; efficacy; migraine; migraine treatment; pharmacokinetics; pharmacology; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: Dr Joshi is on the advisory board for Eli Lilly and Company, Indianapolis, IN, USA, and is on the speakers bureau for Avanir Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Aliso Viejo, CA, USA; Depomed; Pernix Therapeutics, Inc., Morristown, NJ, USA; Allergan Inc., Irvine, CA, USA; Supernus Pharmaceuticals Inc, Rockville, MD, USA; and Teva Pharmaceuticals, Frazer, PA, USA. Dr Rapoport is on the speakers bureau for Avanir and Depomed and is a consultant to Autonomic Technologies, Inc., Redwood City, CA, USA; Avanir; Depomed; Dr Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd., Princeton, NJ, USA; electroCore, LLC, Basking Ridge, NJ, USA; Impax Laboratories, Inc., Bridgewater, NJ, USA; Pernix; Teva; and Zosano Pharma, Fremont, CA, USA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute treatment of migraine attacks: efficacy and safety of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, diclofenac-potassium, in comparison to oral sumatriptan and placebo. The Diclofenac-K/Sumatriptan Migraine Study Group.Cephalalgia. 1999 May;19(4):232-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1999.019004232.x. Cephalalgia. 1999. PMID: 10376168 Clinical Trial.
-
Post Hoc Subanalysis of Two Randomized, Controlled Phase 3 Trials Evaluating Diclofenac Potassium for Oral Solution: Impact of Migraine-Associated Nausea and Prior Triptan Use on Efficacy.Headache. 2017 May;57(5):756-765. doi: 10.1111/head.13073. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Headache. 2017. PMID: 28386945 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
IM ketorolac vs diclofenac potassium powder for oral solution for the acute treatment of severe migraine: a randomized controlled trial.Neurol Sci. 2020 Mar;41(3):537-542. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04157-y. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31833000 Clinical Trial.
-
Diclofenac-potassium in migraine: a review.Drugs. 1999 Jun;57(6):991-1003. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199957060-00016. Drugs. 1999. PMID: 10400409 Review.
-
Diclofenac potassium powder for oral solution: a review of its use in patients with acute migraine.CNS Drugs. 2014 Aug;28(8):761-8. doi: 10.1007/s40263-014-0186-y. CNS Drugs. 2014. PMID: 25034250 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacogenetics in Primary Headache Disorders.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 10;12:820214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.820214. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35222013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: Central and Peripheral Effects of Diclofenac.Pain Ther. 2018 Dec;7(2):163-177. doi: 10.1007/s40122-018-0100-2. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Pain Ther. 2018. PMID: 29873010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diclofenac in the treatment of pain in patients with rheumatic diseases.Reumatologia. 2018;56(3):174-183. doi: 10.5114/reum.2018.76816. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Reumatologia. 2018. PMID: 30042605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CGRP and Migraine: The Role of Blocking Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Ligand and Receptor in the Management of Migraine.Drugs. 2018 Jun;78(9):913-928. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0923-5. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29869205 Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of simple analgesics for acute treatment of episodic tension-type headache in adults: a network meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2357235. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2357235. Epub 2024 May 30. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 38813682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015; 386: 743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang M, Rapoport AM. Acute treatment of migraine headache. Tech Reg Anesth Pain Manag 2009; 13: 9–15.
-
- American Academy of Neurology. Migraine headache, https://www.aan.com/guidelines/home/getguidelinecontent/120 (2016, accessed 15 August 2016).
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013; 33: 629–808. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

