The role of isolated polyethylene exchange in total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 28507777
- PMCID: PMC5420827
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.160049
The role of isolated polyethylene exchange in total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
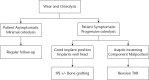
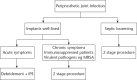
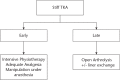
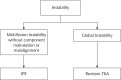
The use of modular total knee arthroplasty (TKA) implants allows surgeons to perform isolated tibial polyethylene insert exchange (IPE) while retaining well-fixed and stable components.The purported advantages of IPE include preservation of bone stock, shorter operating time, less blood loss, faster rehabilitation and lower cost. However, the indications for IPE are limited.IPE for wear and osteolysis has moderate success in the medium term but should be avoided in cases of accelerated wear. In selected cases, debridement and IPE for early infection can result in low morbidity with high success rates in the short term. IPE for arthrofibrosis has poor results.IPE should be undertaken with caution and an institutional algorithm should be followed. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2017;2:66-71 DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.160049.
Keywords: isolated polyethylene exchange; revision; total knee arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of Interest Statement: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical results of modular polyethylene insert exchange with retention of total knee arthroplasty components.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000 Apr;82(4):516-23. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200004000-00007. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000. PMID: 10761942
-
The effectiveness of isolated tibial insert exchange in revision total knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002 Jan;84(1):64-8. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200201000-00010. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. PMID: 11792781
-
Modular insert exchange in knee arthroplasty for treatment of wear and osteolysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007 Nov;464:132-7. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007. PMID: 18062046
-
Total knee arthroplasty using hinge joints: Indications and results.EFORT Open Rev. 2019 Apr 25;4(4):121-132. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.4.180056. eCollection 2019 Apr. EFORT Open Rev. 2019. PMID: 31057949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arthroscopic treatment of total knee arthroplasty complications.EFORT Open Rev. 2019 Feb 13;4(2):33-43. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.4.180035. eCollection 2019 Feb. EFORT Open Rev. 2019. PMID: 30931147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Late-Onset De Novo Genu Recurvatum after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Potential Indication for Isolated Polyethylene Exchange.Arthroplast Today. 2020 Jul 13;6(3):492-495. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2020.05.014. eCollection 2020 Sep. Arthroplast Today. 2020. PMID: 32685642 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudogout After Total Knee Arthroplasty Meeting Minor Criteria for Infection Treated by Polyethylene Exchange.Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2023 Jan 28;15:67912. doi: 10.52965/001c.67912. eCollection 2023. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2023. PMID: 36776277 Free PMC article.
-
Fracture of the polyethylene tibial post in the posterior-stabilized total knee prosthesis: arthrographic and CT arthrographic diagnosis.Skeletal Radiol. 2019 Jul;48(7):1145-1148. doi: 10.1007/s00256-019-03173-5. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Skeletal Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30729263
-
The Role of Constraint in Revision Total Knee Replacement for Instability: Full Component Revision Vs Isolated Polyethylene Exchange in Selected Patients.Arthroplast Today. 2023 Apr 25;21:101134. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2023.101134. eCollection 2023 Jun. Arthroplast Today. 2023. PMID: 37193537 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Isolated Tibial Insert Exchanges for Global Instability to Full Revisions for Flexion Instability in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty.Arthroplast Today. 2025 Jul 29;34:101782. doi: 10.1016/j.artd.2025.101782. eCollection 2025 Aug. Arthroplast Today. 2025. PMID: 40787590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robertsson O, Dunbar M, Pehrsson T, Knutson K, Lidgren L. Patient satisfaction after knee arthroplasty: a report on 27,372 knees operated on between 1981 and 1995 in Sweden. Acta Orthop Scand 2000;71:262-267. - PubMed
-
- Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri S, Jacoby SM. Insall Award paper. Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002;404:7-13. - PubMed
-
- Abdel MP, Morrey ME, Jensen MR, Morrey BF. Increased long-term survival of posterior cruciate-retaining versus posterior cruciate-stabilizing total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 2011;93-A:2072-2078. - PubMed
-
- No authors listed. Swedish Knee Arthroplasty Register Annual report 2010. http://www.myknee.se/pdf/114_SKAR2010_Eng1.0.pdf (date last accessed 22 February 2017).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

